Relation between 2-D Euclidean system and Homogeneous coordinate system
Suppose that P(x,y) be any point in 2-D Euclidean system. In HCS, we add a third coordinate to the point. In place of (x,y), all points are represented via a triple (x,y,H) so H≠0; along with the condition as (x1,y1,H1)=(x2,y2,H2) ↔ x1/H1 = x2/H2 ; y1/H1 = y2/H2. In two dimensions the value of H is generally remained at 1 for simplicity. If we take H=0 now, then this presents point at infinity, which is generation of horizons.
The subsequent table demonstrates an association between 2-D Euclidean (Cartesian coordinate) system and Homogeneous coordinate system.
2-D Euclidian System Homogeneous Coordinate System (HCS)
Any point (x,y) → (x,y,1)
If (x,y,H) be any point in HCS(such that H≠0);
then (x,y,H)=(x/H,y/H,1), which is
(x/H,y/H) ← (x,y,H)
Any one point (x,y) → (x+tx,y+ty) in 2-D Euclidian system. By using Homogeneous coordinate system, this translation transformation can be presented as (x,y,1) → (x+tx,y+ty,1). In two dimensions the value of H is generally maintained at 1 for simplicity. Here, we are capable to represent this translation transformation in matrix form as:
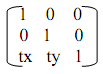
(x',y',1)=(x,y,1)
P'h=Ph.Tv
Here P'h and Ph demonstrate here object points in Homogeneous Coordinates and Tv is termed as homogeneous transformation matrix for translation. Consequently, P'h, the new coordinates of a transformed object, can be determined by multiplying earlier object coordinate matrix, Ph, along with the transformation matrix for translation Tv.
The benefit of initiating the matrix form of translation is to simplify the operations on complicated objects which are, we can now build complicated transformations by multiplying the basic matrix transformations. Such process is termed as concatenation of matrices and the resulting matrix is frequently referred as the composite transformation matrix.