Image Processing
New digital technology has made this possible for the manipulation of multi- dimensional signals along with systems which range from easy digital circuits to advanced parallel computers. The objective of this manipulation can be divided into three categories:
1) Image Processing image in -> image out
2) Image Analysis image in -> measurements out
3) Image Understanding image in -> high-level description out
We will focus upon the fundamental ideas of image processing. We can only create many introductory remarks regarding image analysis here, since to go into details would be beyond the scope of this section. Image understanding needs an approach which is different fundamentally from the theme of this section. Additionally, we will limit ourselves to two-dimensional or 2D image processing though; mainly the ideas and techniques which are to be illustrated can be extended simply to three or more dimensions.
We begin along with specific basic definitions. An image explained in the "true world" is considered to be a function of two real variables, for illustration, a(x,y) along with a as the amplitude for example: brightness, of the image at the actual coordinate position (x,y). An image might be considered to include sub-images occasionally referred to as areas-of-interest, ROIs or only regions. This idea reflects the information that images often contain collections of objects each of that can be the basis for an area. In a sophisticated image processing system this should be probable to apply exact image processing operations to selected regions. Therefore, one part of an image or region might be processed to suppress motion blur while the other part might be processed to enhance colour rendition.
The amplitudes of a specified image will mostly always be either true numbers or integer numbers. The latter is generally a result of a quantization process which converts a continuous range as between 0 and 100 percent to a discrete number of levels. In specific image-forming processes, conversely, the signal may engage photon counting that implies the amplitude that would be inherently quantized. In other image forming procedures, as magnetic resonance imaging, the direct physical measurement yields a complicated number in the form of a real phase and a real magnitude.
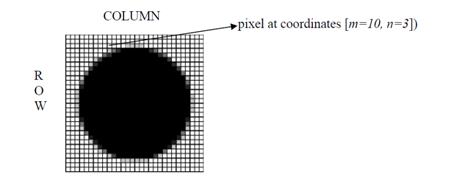
A digital image a[m,n] illustrated in a two dimensional discrete space is derived from an analog image a(x,y) in a two dimensional continuous space by a sampling process which is frequently referred to as digitization.
Now let us discuss details of digitization. The two dimensional continuous image a(x,y) is divided into N rows and M columns. A row and a column, both intersections are termed a pixel. The value allocated to the integer coordinates [m,n] along with {m=0,1,2,...,M -1} and {n=0,1,2,...,N -1} is a[m,n]. Actually, in most cases a(x,y): that we might think to be the physical signal that impinges upon the face of a two dimensional sensor, is in fact a function of many variables comprising depth (z), colour (l), and time (t). The consequence of digitization is demonstrations in following figure.