Structure of an Object Type:
Similar to package, an object type has 2 parts: the specification and the body. The specification is the interface to your applications; it declares a data structure (that is, a set of attributes) along with the operations required to operate the data. The body fully explains the methods, and therefore implements the specification.
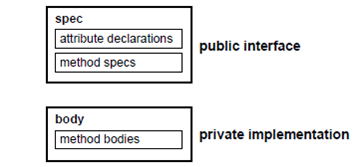
Figure: Object Type Structure
All the information a client program require to use the methods is in the specification. Imagine of the specification as an operational interface and of the body as the black box. You can debug, replace, or enhance the body without changing the enhance -and without affecting the client programs.
In an object type specification, all the attributes should be declared before any methods. The subprograms only have a fundamental implementation. As a result, if an object type specification declares only the attributes, the object type body is needless. You cannot declare attributes into the body. All the declaration in the object type specification is public.
To recognize the structure enhanced study the illustration below, in which an object type for the complex numbers is explained. For now, it is adequate to know that the complex number has two sections, a real part & an imaginary part, and that quite a few arithmetic operations are defined for complex numbers.
CREATE TYPE Complex AS OBJECT (
rpart REAL, -- attribute
ipart REAL,
MEMBER FUNCTION plus (x Complex) RETURN Complex, -- method
MEMBER FUNCTION less (x Complex) RETURN Complex,
MEMBER FUNCTION times (x Complex) RETURN Complex,
MEMBER FUNCTION divby (x Complex) RETURN Complex
);
CREATE TYPE BODY Complex AS
MEMBER FUNCTION plus (x Complex) RETURN Complex IS
BEGIN
RETURN Complex(rpart + x.rpart, ipart + x.ipart);
END plus;
MEMBER FUNCTION less (x Complex) RETURN Complex IS
BEGIN
RETURN Complex(rpart - x.rpart, ipart - x.ipart);
END less;
MEMBER FUNCTION times (x Complex) RETURN Complex IS
BEGIN
RETURN Complex(rpart * x.rpart - ipart * x.ipart,
rpart * x.ipart + ipart * x.rpart);
END times;
MEMBER FUNCTION divby (x Complex) RETURN Complex IS
z REAL := x.rpart**2 + x.ipart**2;
BEGIN
RETURN Complex((rpart * x.rpart + ipart * x.ipart) / z,
(ipart * x.rpart - rpart * x.ipart) / z);
END divby;
END;