Q. Show the Halides of Aluminium?
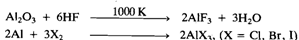
All the four trihalides of aluminium, i.e. AIF3, AICI3,, AlBr3, and AlI3, are known. AIF3, is made by treating Al203 with HF gas at 1000 K and the other trihalides are prepared by the direct exothermic reaction of the elements, e.g:
AlCl3 is also obtained by heating a mixture of alumina and coke in a current of Cl2:
Al203 + 3C + 3Cl2-------------------------------> 2AlCl3 + 3C0
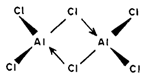
Aluminium trifluoride differs from the other trihalides of Al in being ionic and nonvolatile in nature. Other halides of Al, as also of Ga and In, are covalent in nature when anhydrous and are relatively more volatile. AlCI3, AlBr3, and AlI3, exist as dimeric species formed by pairing of two AIX3 units as shown in Fig, 6.5. The pairing occurs by formation of a coordinate covalent bond from the halogen on one AlX3 unit to the Al atom of another. Thus, for AlCl3, the species Al2CI6, is formed. This is similar to the linking together of BeCI2, units in solid BeCl2, which you have already studied in the preceding unit.
The dimidiation of AlX3, occurs because these halides are electron deficient. By dimidiation, the halides attain' an octet of electrons. You have studied that the trihalides, BX3 are also electron deficient and attain an octet by p?-p? bonding. This is not possible in case of A1 and other larger elements because-of lack of efficient. ?-overlap, and hence, they dimerise. This dimidiation is retained when the halides dissolve in non-polar solvents such as C6H6 and CCl3. In coordinating solvents, such as, diethyl ether, trimethyl amine and phosphorus oxochloride, AlCl3, forms complexes like AlCl3.0Et3, AlCI3, .NMe3, and AlCl3.OPCl3, e.g.:
Al2Cl6 + 2(C2H5)2O----------------------------------> 2 (C2H5)20AlCl3
Alkyl and acyl chlorides, RCI and RCOCl, react with AlCl3 to form complexes of the type R+AICI-4, and RCO+AICI-4, respectively; these are formed as intermediates in Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions.