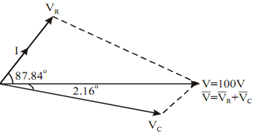
Phasor relation between different voltages and currents:
In the capacitive circuit of Figure, find
1. Impedance,
2. Resultant current,
3. Power factor,
4. Power absorbed by the circuit, and
5. Phasor relation between different voltages and currents.
Figure
Solution
(a) The capacitive reactance is given by
X C = 1 / ωC = 1/2π fC
= 1 / (2π× 50 × 1 × 10- 6)
= 3182.68 Ω
So the impedance, Z = R -j X C
= 120 - j 3182.68 Ω
In polar form, Z = 3184.94 ∠ - 87.84o Ω
(b) Resultant current
i = v/ Z = 100 ∠ 0o / 3184.94 ∠- 87.84o
= 0.03139 ∠ 87.84o Amp (leading)
(c) Power factor, cos φ = cos 87.84o
= 0.0376 (lead)
(d) Power is absorbed only by resistor and that is also known as the active power in the circuit
P = I 2 R
= (0.03139)+ × 120
= 0.1182 Watts
(e) Voltage drop across resistor :
VR = iR
= 0.03139 ∠ 87.84o × 120
= 3.7668 ∠ 87.84o Volt (in phase with current i)
Voltage drop across capacitor
Vc = i (- j X c )
= 0.03139 ∠ 87.84 × 3182.68 ∠ - 90o
= 99.9 ∠ - 2.16o (lagging)
The phasor diagram is shown in Figure 4.25 and applied Voltage of 100 ∠ 0o is taken as reference.
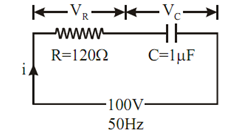
Figure: Phasor Diagram