How Exceptions Propagate ?
Whenever an exception is raised, and if the PL/SQL cannot find a handler for it in the present subprogram or block, the exception propagates. That is, the exceptions reproduce it in the succeeding enclosing blocks until a handler is found or there are no more blocks to search. In the latter situation, the PL/SQL returns an unhandled exception error to the host atmosphere.
Though, exceptions cannot propagate across the remote procedure calls (RPCs). As a result, the PL/SQL block cannot catch an exception raised by a remote subprogram.
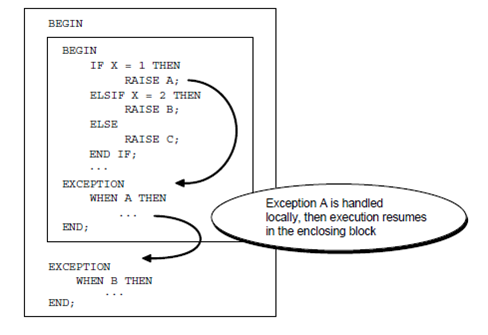
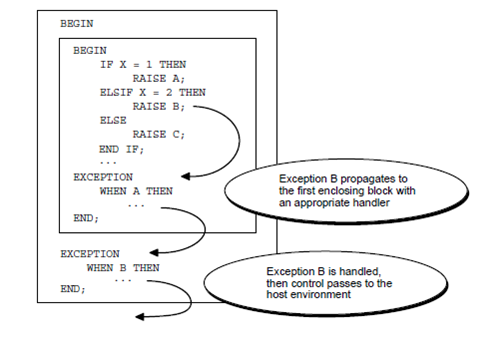
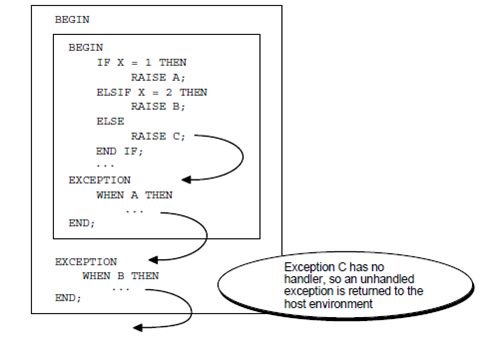
An exception can propagate additional than its scope, that is, additional than the block in which it was declared. Consider the illustration which is as shown below:
BEGIN
...
DECLARE ---------- sub-block begins
past_due EXCEPTION;
BEGIN
...
IF ... THEN
RAISE past_due;
END IF;
END; ------------- sub-block ends
EXCEPTION
...
WHEN OTHERS THEN
ROLLBACK;
END;
As the block in which the exception past_due was declared has no handler, the exception propagates to the enclosing block. But, according to the scope rules, the enclosing blocks cannot reference the exceptions declared in a sub-block. Therefore, only an OTHERS handler can catch the exception.