ENTROPY
Entropy is a thermodynamic property of a system. It is denoted as S and like as the enthalpy and internal energy, it is a state function. In thermodynamic expression, entropy is defined in terms of changes in entropy rather than its absolute value. Any process in any system, under iso-thermal conditions, the change in entropy (dS) is defined as:
dS=dqrev/T (reversible process) dS>dq/T (irreversible process)
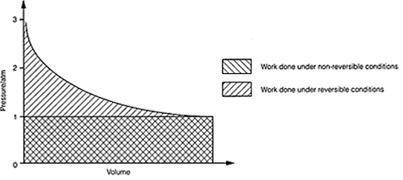
Fig.1. Work done by an expanding gas under reversible and non-reversible
conditions.
The third law of thermodynamics
The third law of thermodynamics states that: "the entropy of a perfectly crystalline solid at the absolute zero of temperature is zero".
For a perfectly crystalline solid, there can be only one possible spatial configuration of the components of the crystal, and as the material is at the absolute zero of temperature, there are no dynamic changes in the crystal either. Under these condition, the total number of possible ways of arranging the material equal one (w=1), and so the entropy (defined as kBlnw) is equal to zero.
ENTROPY AND CHANGE
Second law of thermodynamics:
"The entropy of an isolated system increases for irreversible processes and remains constant in the course of reversible processes. The entropy of an isolated system never decreases".
Any non-equilibrium process leads to a change in entropy. It is a state function; the change may be calculated from the standard entropy of the initial and final states of the system: