Mapping of a Fraction -Windowing Transformations
The mapping of a fraction of a world coordinate scene to device coordinates is considered to as Viewing Transformation. In common 2Dimentional viewing transformations are considered to as window to windowing transformation or viewport transformation.
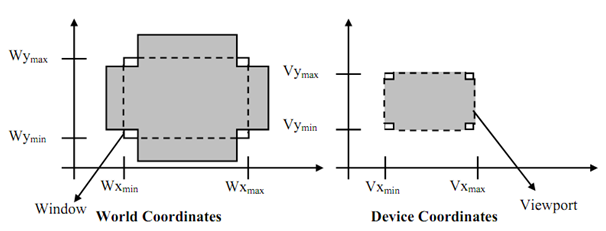
Figure: Windowing Transformation
We can see in above figure, here all parts of the picture which lie outside the window are clipped and the contents that lie within the widow are transferred to device coordinates. Secondly, we can also observe that while window chooses a part of the scene, viewport displays the chosen part at the desired location on the display region. While window is changed we see a dissimilar part of the scene at similar portion as viewport on display. If we modify the viewport only, we notice identical part of the scene drawn at a diverse scale or at a diverse place on the display. By successively decreasing or raising the size of the window around a part of the scene the viewport kept fixed, we can determine the effect of zoom out or in respectively on the displayed part. By mathematically, viewing transformation can be represented as V=W.N
Here,
- V refers Viewing transformation that maps a part of world coordinate scene to device coordinates;
- W refers to workstation transformation that maps normalized device coordinates to physical device coordinates;
- N refers to Normalization transformation utilized to map world coordinates to normalized device coordinates.
Window to Viewpoint Coordinates transformation:
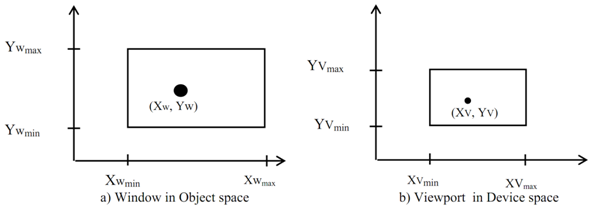
Figure: Window to Viewport Transformation
Figure as shown in above, demonstrates window-viewpoint mapping. Now, it is depicted here a point at position (Xw, Yw) in window is mapped on position (Xv, Yv) in the connected viewpoint.
Consequently, as to keep the same relative placement in the viewpoint like in the window we need:
(xv - xvmin)/( xvmax - xvmin) =(xw - xwmin)/(xwmax - xwmin)..............1(a)
(yv - yvmin)/ (yvmax - yvmin) = (yw - ywmin)/(ywmax - ywmin)................1(b)
Again arranging equation (a) and (b) of (1) we denote viewpoint position (xv, yv) which is:
{ xv = xvmin + (xw - xwmin) Sx
yv = yvmin + (yw - ywmin) Sy }..........................(2)
Here,
Sx scaling factor along x axis = (xvmax - xvmin)/(xwmax - xwmin)
Sy scaling factor along y axis = (yvmax - yvmin)/(ywmax - ywmin).........................................(3)
Note: if Sx = Sy then the relative proportions of objects are preserved else the world object will be contracted or stretched in either x or y direction while displayed on output device.