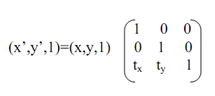Homogeneous Coordinate Systems - 2-d and 3-d transformations
Suppose P(x,y) be any point in 2-D Euclidean (Cartesian) system. In HC System, we add a third coordinate to a point. In place of (x,y), all points are represented via a triple (x,y,H) where H≠0; along with the condition which is (x1,y1,H1)=(x2,y2,H2) ↔ x1/H1 = x2/H2 ; y1/H1 = y2/H2.
Currently, if we take H=0, then we contain point at infinity, that is, generation of horizons.
Hence, (2, 3, 6) and (4, 6, 12) are the similar points are represented by various coordinate triples, that is each point has many diverse Homogeneous Coordinate representation.
|
2-D Euclidian System Homogeneous Coordinate System
|
|
Any point (x,y) (x,y,1)
|
|
If (x,y,H) be any point in HCS(such that H≠0); Then (x,y,H)=(x/H,y/H,1)
|
|
(x/H,y/H) (x,y,H)
|
Currently, we are in the position to build the matrix form for the translation along with the utilization of homogeneous coordinates.For translation transformation (x,y)→(x+tx,y+ty) within Euclidian system, here tx and ty both are the translation factor in direction of x and y respectively. Unfortunately, this manner of illustrating translation does not utilize a matrix; consequently it cannot be combined along with other transformations by easy matrix multiplication. That type of combination would be desirable; for illustration, we have observed that rotation about an arbitrary point can be done via a rotation, a translation and the other translation. We would like to be capable to combine these three transformations in a particular transformation for the sake of elegance and efficiency. One way of doing such, is to utilize homogeneous coordinates. In homogeneous coordinates we utilize 3x3 matrices in place of 2x2, initiating an additional dummy coordinate H. In place of (x,y), each point is demonstrated by a triple (x,y,H) here H≠0; In two dimensions the value of H is generally set at 1 for simplicity.
Hence, in homogeneous coordinate systems (x,y,1) → (x+tx,y+ty,1), now, we can simplifies this in matrix form like: