What is Mitochondria ?
Mitochondria are the cellular organelles responsible for the conversion of energy into a form called ATP. ATP is a high energy chemical compound that cells use to carry out all of their various activities. These activities include everything a cell does, such as building and repairing cell structures, movement, reproduction, making products for use elsewhere, breaking down food, and performing whatever specialized function the cell might have.
This conversion of energy to ATP, the primary source of energy for chemical reactions in living cells, is called cellular respiration. ATP stands for the abbreviation of a compound called adenosine triphosphate. Accordingly, mitochondria are more numerous in cells that use a lot of energy, such as muscle cells.
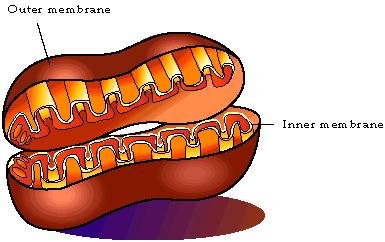
Each mitochondrion has an outer membrane, and an inner membrane with folds called cristae. The cristae are where the chemical reactions associated with cellular respiration take place.
One interesting fact is that mitochondria have their own DNA, which is separate and distinct from the DNA that is associated with the nucleus. In addition, during cell division, the mitochondria in the cytoplasm divide independently from the nucleus. Proteins are synthesized from the mitochondrial DNA using mitochondrial ribosomes, which are actually smaller than those of eukaryotes, and are similar to those of prokaryotes. The polypeptides that are made from the mitochondrial DNA do not form complete enzymes, but form subunits that are used in ATP synthesis.
Since new mitochondria can come only from existing mitochondria, some scientists have suggested that mitochondria were originally free-living prokaryotes. According to this theory, a bacteria-like cell might have been ingested by another cell, and then because of a resulting symbiotic mutual benefit, was retained by the ingesting cell. Eventually the ingested cell became incorporated and evolved into what we now call mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. Strangely, one eukaryotic organism, the parasite Giardia lamblia, has cells that do not contain mitochondria at all. A similar type of evolution involving blue-green bacteria may have occurred to form chloroplasts.