Q. What do you mean by Magnetic circuits?
A magnetic circuit provides a path for magnetic flux, just as an electric circuit provides a path for electric current.Magnetic circuits are integral parts of transformers, electric machines, and many other common devices such as doorbells. Analogous to voltage (electric potential difference) in the electric circuit, in a magnetic circuit we have the magnetomotive force (mmf), or the magnetic potential difference which produces a magnetic field, and which has units of amperes or ampere turns. The two sources of mmf in magnetic circuits are the electric current and the permanent magnet (which stores energy and is capable of maintaining a magnetic field with no expenditure of power). The current source is commonly a coil of N turns, carrying a current I known as the exciting current; the mmf is then said to be NI At.
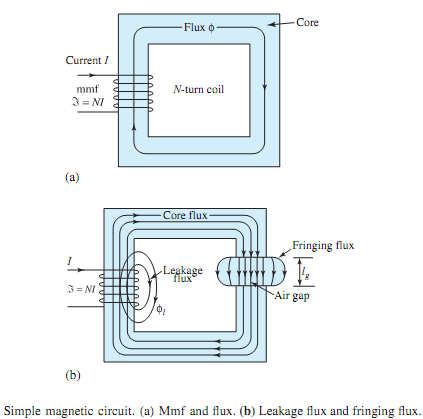
Figure (a) shows, schematically, a simple magnetic circuit with an mmf ℑ� (= NI) and magnetic flux φ. Note that the right-hand rule gives the direction of flux for the chosen direction of current. The concept of a magnetic circuit is useful in estimating the mmf (excitation ampere-turns) needed for simple electromagnetic structures, or in finding approximate flux and flux densities produced by coils wound on ferromagnetic cores.Magnetic circuit analysis follows the procedures that are used for simple dc electric circuit analysis. Calculations of excitation are usually based on Ampere's law, given by
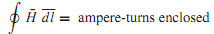
where H(| ¯H|= B/µ) is the magnetic field intensity along the path of the flux. If the magnetic field strength is approximately constant (H = HC) along the closed flux path, and lC is the average (mean) length of the magnetic path in the core, Equation can be simplified as
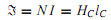
Analogous to Ohm's law for dc electric circuits, we have this relation for magnetic circuits,
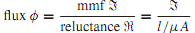
where µ is the permeability, A is the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of l, and l stands for the corresponding portion of the length of the magnetic circuit along the flux path. Based on the analogy betweenmagnetic circuits and dc resistive circuits, Table summarizes the corresponding quantities. Further, the laws of resistances in series and parallel also hold for reluctances.