The stability of a complex relies on
1. Nature of central ion: the word nature means the charge density on the central ion i.e. greater is the charge density or larger the charge/radius ratio more is the stability of a complex. For example, out of complexes of Fe2+ and Fe3+, are more stable.
For example,
Fe3+ + 6CN- 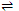 [Fe(CN)6]3-; K = 1.2 × 1031
[Fe(CN)6]3-; K = 1.2 × 1031
Fe2+ + 6CN- 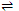 [Fe(CN)6]4- ; K = 1.8 × 106
[Fe(CN)6]4- ; K = 1.8 × 106
For the ions which carry the same charge the one with a smaller size the more stable complexes. For example, among Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Fe2+ complexes as the size of copper is the smallest therefore it gives the most stable complexes.
2. Nature of ligand
(a) Basic character of ligands: more basic is a ligand, greater is the ease with which it can donate its electrons and therefore more is the stability of the complex. For example, the complexes involving F- ions are more stable than those involving Cl- ions or Br- ions.
(b) Charge on ligands: for charged ligands, the higher the charge and the smaller their size, the more stable are the complexes.
(c) Chelate effect: also complexes containing chelate rings are usually more stable than similar complexes containing no rings. This is termed as chelate effect.
For example,
Ni2+(aq) + 6NH3(aq) ? [Ni(NH3)6]2+(aq) log 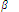 = 7.99
= 7.99
Ni2+(aq) + 3 en(aq) ? [Ni(en)3]2+(aq) log 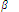 = 18.1
= 18.1
3. Crystal field effects (Irving-William Order): the stability of high spin complexes of the ions between Mn2+ and Zn2+ with a given ligand frequently vary in the order:
Mn2+ < Fe+2 < Co+2 < Ni2+ < Cu+2 > Zn+2
This order is also called natural order and is consistent with charge to radius ratio concept. Radii of these ions are:
Mn+2 (0.91 Å); Fe+2 (0.83 Å); Co+2 (0.82 Å); Ni+2 (0.78 Å); Cu+2 (0.69 Å); Zn+2 (0.74 Å)
4. Class a and class b metals: chatt and Ahrland have classify the metals into three groups i.e. a, b and borderline on the basis of their electron acceptor properties.
(i) Class a metals: H, group 1 (alkali metals), group 2 (alkaline earths), the elements Sc to Cr; Al to Cl; Zn to Br, In, Sb, Sn, I. these metals form stable complexes with ligands containing N, O and F groups.
(ii) Class b metals: Rh, Pd, Ag, Ir, Pt, Au, Hg.
These elements have fully filled d-orbitals and therefore form more stable complexes with ligands whose donor atoms are heavier member of N, O and F groups.
(iii) Border line metals: elements from Mn to Cu, Tl to Po, Mo, Te, Ru, W, Re, Os, Cd. These do not follow a particular stability order.
The stability order of complexes of these elements with ligands follows the following order:
Class a elements:
F- > Cl- > Br- > I- > O > S > Se > Te > N >> P > As > Sb > Bi
Class b elements:
F- < Cl- Br- < I- < O << S ≈ Se ≈ Te < N << P < As < Sb < Bi