TYPES OF SYNOVIAL JOINT -
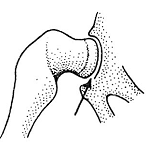
1. BALL AND SOCKET JOINT -
One bone forms a ball like head that fits into a socket formed in the other bone.
Movement is possible in all directions e.g. humerus and pectoral girdle.
2. HINGE JOINT -
The joint allows movement in one plane only, eg. knee joint, elbow joint, ankle joint and joint between phalanges.
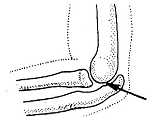
3. ANGULAR, ELLIPSOID OR CONDYLOID JOINT -
It allows movement in 2 directions, side to side and back to forth. oval condyle of one bone fits to concavity of other bone e.g. skull & vertberae.
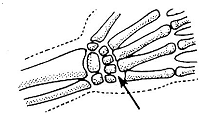
4. GLIDING -
It permits sliding movment of two bones on each other, eg. in wrist, in ankle.
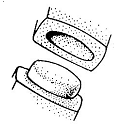
5. PIVOT JOINT -
It allows only a rotary movment of the one bone on the other, which remains stationary. e.g. between atlas and axis vertebrae, between head of radius and capitulum of humerus.
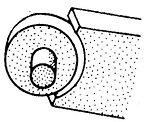
6. SADDLE JOINT -
It resembles to ball and sucket but less developed e.g. between meta carpel and carpel of thumb.