Surface Area- Applications of integrals
In this part we are going to look again at solids of revolution. We very firstly looked at them back in Calculus I while we found the volume of the solid of revolution. In this part we wish to find the surface area of this region.
Thus, for the purposes of the derivation of the formula, let us look at rotating the continuous function
y = f (x) in the interval [a, b]
about the x-axis. Below is an outline (sketch) of a function and the solid of revolution we obtain by rotating the function about the x-axis.
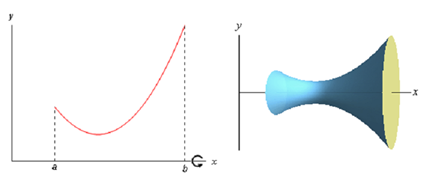
We can obtain a formula for the surface area much more like we derived the formula for arc length. We'll initiate by dividing the integral into n equal subintervals of width Πx. On each subinterval we will estimated the function with a straight line that agrees along with the function at the endpoints of the each interval. Below is a sketch (figure) of that for our representative function using n=4.
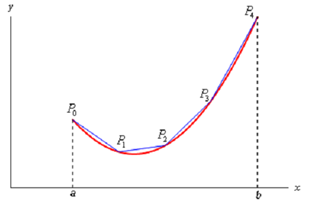
Here, rotate the approximations about the x-axis and we get the subsequent solid.
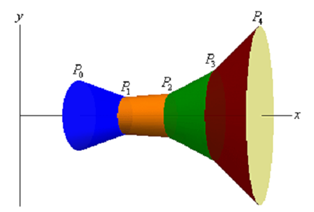
The approximation on every interval provides a distinct portion of the solid and to make this clear every portion is colored differently. Each of these portions are termed as frustums and we know how to find out the surface area of frustums. The surface area of a frustum is illustrated by,
A = 2πrl
r = ½ (r1 + r2)
r1 = radius of right end
r2 = radius of left end
the length of the slant of the frustum.
For the frustum on the interval [xi-1, x1] we contain,
R1 = f(xi)
R2 = f(xi-1)
l = |Pi-1 Pi| (length of the line segment connecting pi and pi-1)
and we know from the preceding section that,
|Pi-1 Pi| = √ 1 + [f' (xi*)]2 Πx
where xi* is some point in,
[Xi-1, Xi]
Previous to writing down the formula for the surface area we are going to presume that Πx is "small" and since f(x) is continuous we can then assume that,
F (xi) » f (xi*) and f (xi-1) » f (xi*)
Thus, the surface area of the frustum on the interval [Xi-1, Xi] is approximately,
Ai = aΠ (f (xi) + f (xi-1) / 2) |pi-1 pi |
» 2Π f (xi*) √ 1+ [f'(xi*)]2 Πx
After that the surface area of the whole solid is approximately,
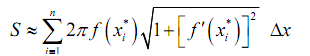
and we can obtain the exact surface area by taking the limit as n goes to infinity.
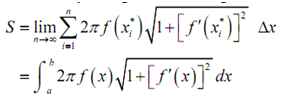
If we wish to we could as well derive a similar formula for rotating x = h(y) on [c,d] about the y-axis. This would provide the following formula.
S = ∫dc 2Π h (y) √ (1+ [h' (y)]2) dy
Though, these are not the "standard" formulas. Note: The roots in both of these formulas are nothing much more than the two ds's we employed in the previous section.
As well, we will replace f(x) with y and h(y) with x. By doing this gives the following two formulas for the surface area.