Reliable data transfer over a channel bit error rdt : 20
A more realist model of the underlying channel is one in which bits in packet may be computed. Such bit errors typically occurs in the physical components of a network as a packet is transmitted propagates or is buffered.
Before developing a protocols for reliably communication over such a channel receiver might say ok after each sentence has bee beard understood an recorded. It the receiver hears a garbled sentence he asked to repeat the garbled sentence, this message dictation protocols uses both positive acknowledgment and negative acknowledgments these control messages allows receiver correctly and what has been received in error and thus requires repeating.
Figure shows the FSM representation of rdt 2.0 a data transfer protocols employing error detection positive acknowledgments and negative acknowledgments.
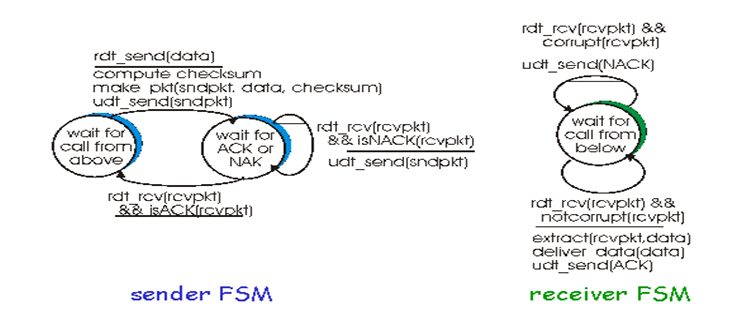
Figure rdt 2.0 FSM specification
The send side of rdt 2.0 has two states. In the left state the send side protocols is waiting for data to be passed down form the upper layer when the rdt send event occurs the sender will create a packet containing the data to be sent along with a packet checksum and then send the packet via duct send operation. In the right most state the sender protocols is waiting for an ACK or a NACK packet from the receiver. If an ACK packet is received. The sender knows that the most recently transmitted packet has been received correctly and thus the protocols returns to the state of waiting for data from the upper layer. If a NACK is received the protocols retransmits that last waits for an ACK or NACK to be returned by the receiver in response to the retransmitted data packet. It is important to note that when the sender is in the wait for ACK or NACK state it cannot get move data from the upper layer that is the rdt send event cannot occur that will happen only after the sender receives an ACK and leaves this state. Thus the sender will not send a new piece of data until. It is sure that the receiver has correctly received the current packet because of this behaviour protocols such as rdt 2.0 are known as stop and wait protocols.
The receiver side FSM for rdt 2.0 still has a single state on packet arrival the receiver replies with either an ACK or a NACK. Depending on whether not the received packet in corrupted. In figure the notation rdt rev and corrupt corresponds to the event in which a packet is received and is found to be in error. Protocols rdt 2.0 many look as if it works but unfortunately it has a fatal flaw or may be possible that the ACK or NACK packet could be corrupted.
Possibilities for handling corrupted ACKs or NACKs
a.For the first possible it the sender didn't understand the ok or please repeat that reply from the receiver the sender would probably ask what did you say? The sender would then repeat the reply. But what if the speaker what did you say? Is corrupted the receiver having no idea whether difficult to understand the garbled sentence was part of the dedication or a request to repeat he last reply, would probably then respond with did you say? And then of course that response might be garbled.
b.A second alternative is to enough checksum bits to allow the sender not only to defect but also to recover from bit errors. This solves the immediate problem for a channel that can corrupt packets but not lose them.
c.A third approach is for the sender simply resend the current data packet when it receives a garbled ACK or NACK packet. This approach introduces duplicate packets into the sender to receiver channel. The fundamental problem with duplicate packets is that the receiver doesn't know whether the ACK or NACK it last sent was received correctly at eh sender. To handling the duplicate packets sender. Sender adds sequence number to each packet retransmits current packet if ACK / NACK garbled receiver discards duplicate packets.