Physical Tests on Cement
(a) Soundness Test: by sieve analysis, it is conducted. 100 gms of cement is taken and sieved throughout IS sieve No. 9 for fifteen minutes. Residue on the sieve is weighed. It should not exceed 10 %by weight of sample taken.
(b) Setting Time: Initial setting time and final setting time are 2 important physical properties of cement. Initial setting time is the time taken by the cement from adding of water to the beginning of losing its plasticity. the time lapsed from adding of the water to full loss of plasticity is called Final setting time. Vicat apparatus is utilized for finding the setting times .Vicat apparatus consists of a movable rod to which any one of the three needles indicate in figure can be attached. An indicator is attaching to the movable rod. A vicat mould is linked with this apparatus which is in the form of split cylinder.
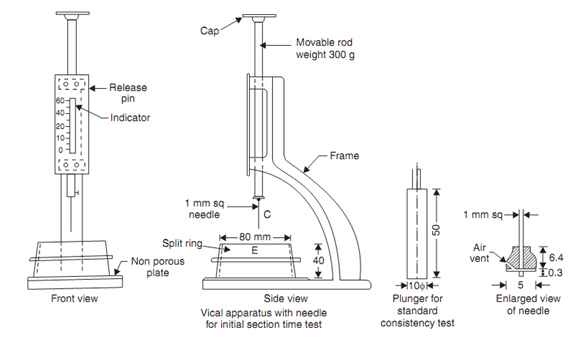
Vicat apparatus
It is necessary to determine water to be added to get standard consistency before finding initial and final setting time. For this 300 gms of cement is mixed with approximate 30% water and cement paste prepared is filled in the mould which rests on non porous plate. The plunger is associated to the movable rod of vicat apparatus and gently lowered to touch the paste in the mould. Then the plunger is permitted to move freely. If the penetration is 5 mm to 7 mm from the bottom of the mould, then cement have standard consistency. If not, experiment will repeat with different proportion of water fill water needed for standard consistency is found. Then the tests for initial and final setting times may be carried out as described below:
Initial Setting Time: 300 gms of cement is comprehensively mixed with 0.85 times the water for standard consistency and vicat mould is fully filled and top surface is leveled. 1 mm square needle is fixed to the rod and gently placed over the paste. Then it is freely permitted to penetrate. In the starting the needle penetrates the paste fully. As time lapses the paste start losing its plasticity and offers resistance to penetration. When needle may penetrate up to 5 to 7 mm above bottom of the paste experiment is stopped and time elapsed between the addition of water and end I f the experiment is noted down as initial setting time.
Final Setting Time. The square needle is replaced with annular collar. Experiment is continued by permitting this needle to freely move after gently touching the surface of the paste. Time elapsed among the addition of water and the mark of needle but not of annular ring is found on the paste. This time is noted down as final setting time.
(c) Soundness Test: This test is conducted to find free lime in cement, which is not wanted. Le Chatelier apparatus shown in given figure is used for conducting this test. It consists of a split brass mould of height 30 mm and diameter 30 mm. On either side of the split, there are 2 indicators, with pointed ends. The ends of indicators are 165 mm from the centre of the mould.
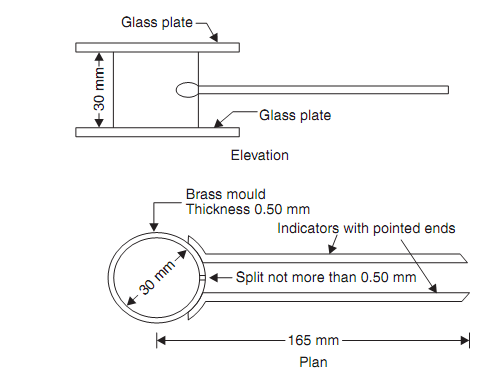
Le Chatelier's apparatus
Correctly oiled Le Chatelier mould is placed on a glass plate and is filled fully with a cement paste with 0.78 times the water needed for standard consistency. It is then covered with another glass plate and a small weight is placed over it. Then the entire assembly is kept under water for 24 hours. The temperature of water should be between 24°C and 50°C. Note down the distance between the indicators. Then place the mould again in the water and heat the assembly like that water reaches the boiling point in 30 minutes. Boil the water for 1 hour. The mould is removed from water and permitted to cool. The distance between the 2 pointers is measured. The difference among the two readings indicates the expansion of the cement due to the presence of unburnt lime. This value should not exceed from 10 mm.
(d) Crushing Strength Test: For this 200 gm of cement is mixed with 600 gm of standard sand by confirming to IS 650-1966. After mixing comprehensively in dry condition for a minute distilled potable P/4 +3 percentage is added where P is the water needed for the standard consistency. They are mixed along with trowel for 3 to 4 minutes to get regular mixture. The mix is placed in a cube mould of 70.6 mm size (Area 5000 mm2) reserved on a steel plate and prodded with 25 mm standard steel rod 20 times within 8 seconds. Then the mould is placed on a standard vibrating table that vibrates at a speed of 12000 ± 400 vibration per minute. A hopper is safe at the top and the remaining mortar is filled. The mould is vibrated for 2 minutes and hopper removed. The top is over with a knife or with a trowel and leveled. After 24 ± 1 hour mould is removed and cube is placed under clean water for curing.
After particular period cubes are tested in compression testing machine, keeping the specimen on its level edges. Average of 3 cubes is reported as crushing strength. The compressive strength at the end of 3 days shall not be less than 11.5 N/mm2 and that at the end of 7 days not less than 17.5 N/mm2.