Leadership in an Oil Production Game
Students can be broken into pairs to play this game once, witheach student's representing one country; then each shouldswitch partners and play as if she were the other country.Students could also play this game individually, indicatingwhich action they choose when playing as each country; youcan pair sets of answers to show outcomes. This game is based on the Rational-Pigs game in John McMillan's Games, Strategies, and Managers; he uses the Saudi Arabia analogy onpage 14.
Ask students to consider a very simplified version of thesituation facing members of OPEC in the 1970s. In this sim-plified story, we assume that OPEC is made up of only twocountries-Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. Suppose that eachcountry can produce a unit of oil (maybe a million barrels)at a cost of $1. Saudi Arabia is a big country and can pro-duce either 4 or 5 units of oil; Kuwait is a small country andcan produce either 1 or 2 units of oil.
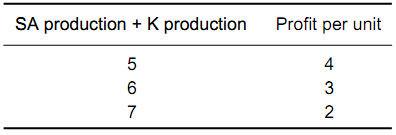
Given output and consumption in the rest of the world,the following formula tells us the price at which oil is sold:Price = 10 - (QS + QK), where QS is the number of unitsproduced by Saudi Arabia (SA), and QK is the number of units produced by Kuwait (K). Then profits are calculated as follows. If SA produces 4 units and K produces 1 unit, theprice of a unit of oil equals 5 (from the above formula). Be-cause the cost of producing a unit of oil equals $1, a countryearns a profit of $4 for each unit it makes. Because SA pro-duces 4 units, its total profit equals $16; because K produces 1 unit, its total profit equals $4. Profit per unit obviouslydepends on total production, as the following table illustrates:
Finally, tell students to put themselves in this situation,tell them to worry only about their own profits, and ask them:(1) How many units would you produce if you were SaudiArabia? (2) How many units would you produce if you were Kuwait?
When discussing this game, you can first collect studentinput on their choices, writing on the board the number of students who chose 4 as Saudi Arabia and 2 as Kuwait. Thenyou can show how the game can be analyzed more formally.It is nice to show that the symmetric version of the game (inwhich Saudi Arabia and Kuwait each choose either 2 or 3units) is a standard prisoners' dilemma; the smaller output level is the cooperative strategy. Once you change the choices available to the playersto be consistent with the description of the game and changethe payoffs accordingly, you will be able to illustrate how the analysis changes. Encourage students to provide hypothe-ses for why Saudi Arabia's incentives have changed andbuild on their ideas to show that large players often incur a much higher cost of cheating than do small players. Ask students to think of other examples of dilemma situations with leadership or provide some of your own.