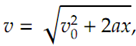Kinematics Equations
Kinematics deals with problems involving distance, velocity, time and constant acceleration. The restraint that acceleration is a constant for these problems limits the scope of this subject, but a large body of applications remains. Vector concepts are not generally employed, so that velocity is undirected and equivalent to speed. Distance, denoted by x, refers to the total distance travelled not necessarily the distance between the starting and stopping points. Force and mass aren't involved in the kinematics relations.
The first equation relates the distance covered by an object during some time interval. As the acceleration may be non-zero the velocity may vary during the time interval under consideration.
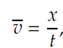
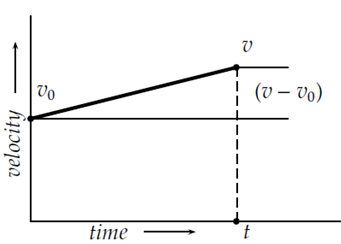
The mainly useful relation is where  the average velocity is x is the total distance with t is the elapsed time. Given that acceleration is to be constant velocity perhaps uniformly decreasing or increasing. A plot presenting the case of increasing velocity is shown in
the average velocity is x is the total distance with t is the elapsed time. Given that acceleration is to be constant velocity perhaps uniformly decreasing or increasing. A plot presenting the case of increasing velocity is shown in
The relation among acceleration and velocity is
a = v- v0/t
, or
v = v0 + at
Where v is the final velocity subsequent to the specified time has elapsed, v0 is the initial velocity and a is the (constant) acceleration. The average velocity for this case is
 = v0 +(v - v0/2)= (v + v0)/2
= v0 +(v - v0/2)= (v + v0)/2
Other useful equations can be derived from these elementary relations. It is customary to develop a set of equations which involve only three of the four quantities distance, velocity, acceleration and time. We previously have an equation relating acceleration, time and velocity
An equation involving distance, velocity and time requires substituting for
x = ((v + v0)/2)t
For v to derive an equation relating distance, acceleration and time.
Be able to be rearranged to isolate t and then substituted for t in Eq
For an equation relating velocity, distance and acceleration.
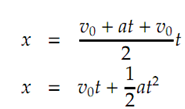
An additionally convenient form for this equation is
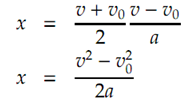
Where v 0 is often zero.