Example Find out all the zeroes of P ( x ) = x4 - 7 x3+ 17 x2 -17 x + 6 .
Solution
We found the list of all possible rational zeroes in the earlier example. Following they are.
±1, ± 2, ± 3, ± 6
Now we have to start evaluating the polynomial at these numbers. We can begin anywhere in the list and will continue till we determine zero.
To perform the evaluations we will build a synthetic division table.
Following is the first synthetic division table for this problem.
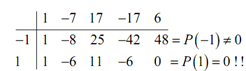
Thus, we found a zero. Before getting into that let's recap the computations to ensure you can do them.
The top row is the coefficients by the polynomial & the first column is the numbers which we're evaluating the polynomial at.
Each of the row (after the first) is the third row from the synthetic division procedure. Let's rapidly look at the first couple of numbers in the second row. In the second column the number is the first coefficient dropped down. In the third column the number is then found by multiplying the -1 by 1 and adding up to the -7. It gives the -8. Then For the fourth number is -1 times -8 added on 17. It is 25, etc.
You can perform regular synthetic division if you have to, but it's a fine idea to be capable to do these tables as it can help with the procedure.
Okay, back to the problem. Now we know that polynomial as, x= 1 is a zero and hence we can write the
P ( x ) = x3 - 7 x3 + 17 x2 -17 x + 6 = ( x -1) ( x3 - 6 x2 + 11x - 6)
Now we have to repeat this procedure with the polynomial Q (x) = x3 - 6 x2 + 11x - 6 . Thus, the first thing to do is to write all possible rational roots of this polynomial & in this case we're fortunate enough to have the first & last numbers in this polynomial be the similar as the original polynomial, usually that won't happen hence don't always expect it. Following is the list of all possible rational zeroes of this polynomial.
±1, ± 2, ± 3, ± 6
Now, before doing a new synthetic division table let's remember again that we are looking for zeroes to P ( x ) & from our first division table we determined that x= -1 is not a zero of
P (x) and therefore there is no cause to bother along with that number again.
It is something that we must always do at this step. Take a look at the list of new possible rational zeros & ask are there any which can't be rational zeroes of the original polynomial. If there are some, throw them out as already we will know that they won't work. Thus, a compact list of numbers to try here is,
1, ±2, ± 3, ± 6
Note that we do have to include x= 1 in the list since this is possible for a zero to take place more that once (that means multiplicity greater than one).
Following is the synthetic division table for this polynomial.
1 -6 11 -6
1 1 -5 6 0 = P (1) = 0!!
Thus, x= 1 is also a zero of Q ( x ) and now we can write Q ( x ) as,
Q ( x ) = x3 - 6 x2 + 11x - 6 = ( x -1) ( x2 - 5x + 6)
Now, technically we could continue the procedure with x2 - 5x + 6 , although this is a quadratic equation and we know how to determine zeroes of these without a complicated procedure like this so let's just solve this like we usually would.
x2 - 5x + 6 = ( x - 2) ( x - 3) = 0
⇒ x=2, x = 3
Notice that these two numbers are in the list of possible rational zeroes.
Finishing up this problem then gives the given list of zeroes for P ( x ) .
x= 1 ( multiplicity 2)
x= 2 ( multiplicity 1)
x= 3 ( multiplicity 1)
Note that x= 1 has a multiplicity of 2 as it illustrated twice in our work above.
Let's also note that we can now completely factor the polynomial P (x ) = x4 - 7 x3 + 17 x2 -17 x + 6 . We know that every zero will give a factor into the factored form & that the exponent onto the factor will be the multiplicity of that zero. Thus, the factored form is,
P ( x ) = x4 - 7 x3 + 17 x2 -17 x + 6 = ( x -1)2 ( x - 2) ( x - 3)