What are the expression trees? Represent the below written expression using a tree.
Give a relevant comment on the result that you get when this tree is traversed in Preorder, Inorder and postorder. (a-b) / ((c*d)+e)
The leaves of an expression tree are operands, for instance constants or variable names, and the other nodes include operators. This particular tree happens to be a binary tree, because all of the operations are binary, and although this is the easiest case, it is probable for nodes to have more than two children. It can also be possible for a node to have only one child, as is the case with the unary minus operator. We can evaluate the expression tree, T, by applying the operator at the root of it to the values obtained by recursively evaluating the left and right subtrees.
The expression tree obtained for the expression: (a - b ) / ( ( c * d ) + e))
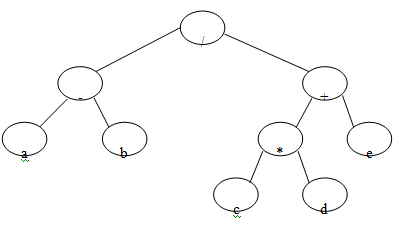
The traversal of the above drawn expression tree gives the following result:-
Preorder:- ( / - a b + * c d e)
This expression is the same as the "prefix notation" of the original expression.
Inorder:- ( a - b) / ((c * d) + e )
Thus the inorder traversal gives us the actual expression.
Postorder:- ( a b - c d * e + / )
Thus the postorder traversal of this gives us the "posfix notation" or we can say the "Reverse Polish notation" of the original expression.