Explain the Mendel's Laws in genetics?
Based on the results of his experiments, Mendel proposed three laws regarding the inheritance of traits: the Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, and the Law of Dominance.
The first principle proposed by Mendel, the Law of Segregation, states that "factors" responsible for inheritance of traits remain separate in the offspring, rather than blending . Because traits not apparent in the F1 generation reappeared in the F2 generation, and the F2 generation also had two factors, Mendel concluded that each parent carried two factors that segregate, or separate, during the formation of sperm or egg cells so that they each carry only one factor; therefore the offspring had two factors, the same as the parent.
Since Mendel studied a number of traits, he found that alleles governing different traits, such as position of flowers along the stem; position, shape, and color of the pod; height of the plant; seed texture, seed color, and seed coat color, segregate independently from the alleles that govern another trait. This formed the basis of the second principle, the Law of Independent Assortment. We will see that this law applies only to genes found on different chromosomes.
The third principle, the Law of Dominance, was a result of Mendel's discovery that when two strains were cross-pollinated, one factor in a pair, the dominant factor, may mask the other, so that the dominant trait is always observed in the F1 generation. He called a factor recessive if the trait did not appear until the F2 generation. Some traits were found to exhibit incomplete dominance; that is, heterozygous plants had phenotypes intermediate between the dominant and the recessive. An example is a dominant red flowered plant and recessive white-flowered producing pink-flowered offspring. If dominant traits produce different phenotypes, and both appear in heterozygotes, the traits are called codominant.
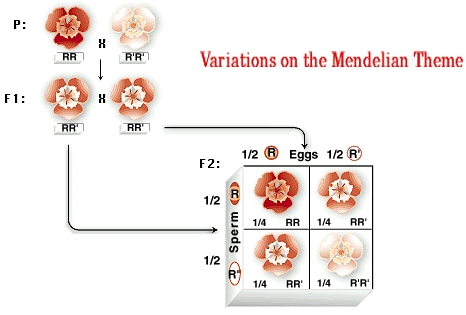
There are traits such as skin color in humans that have more than two phenotypes and result from contributions from two or more genes. This condition is called polygenic inheritance. In its simplest form, two genes code for the same trait; an example is kernel color in wheat, where two genes have two alleles, R for red pigment and R' for no pigment at all. The resulting phenotypes exhibit incomplete dominance as with heterozygous single alleles, but there are more shades of red because there are more genes contributing to the trait.