Determine the loss-by-defect and loss-by-dispersion
Given, Annual production = 1,00,000 units
Specification = 20 ± 4 i.e. m = 20, Δ = 4
Cost of repairing or resetting a product out-of-specification is Rs. 100.
a. Process I,
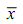 = 20, σ = 1.33
= 20, σ = 1.33
b. Process II,
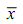 = 18, σ = 0.66
= 18, σ = 0.66
c. Process III,
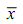 = 17, σ = 0.40
= 17, σ = 0.40
Determine the loss-by-defect and loss-by-dispersion.
Solution
Process I
Given specifications 20±4
∴ USL = 24
LSL = 16
Given process average (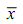 ) is mean
) is mean
centred at target m = 20 and σ = 1.33.
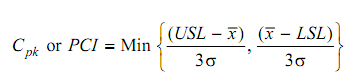
= Min {24 - 20 /3 × 1.33, 20 - 16 /3 × 1.33}
As both values are equal, we might use either of them as minimum value.
∴ C pk = 4/ (3 × 1.33) = 1
Loss-by-defect
Loss = proportion out of specification × total number × cost of product
= 0.0027 × 1,00,000 × 100
= 0.27 × 1,00,000
Loss-by-dispersion
Loss = Loss per piece × number of products
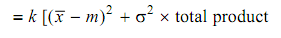
k = A/ Δ2 = 100/42 = 6.2
Process II
∴ Loss = 6.2 [(20 - 20)2 + 1.332] × 1,00,000
= 10.97 × 1,00,000
The process average is observed to be centred at 18 with σ = 0.66
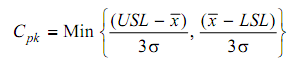
= Min { 24 - 18 /3 × 0.66 , 18 - 16/3 × 0.66}
C pk = 18 - 16 / 3 × 0.66 = 1.01 ≈ 1
Loss-by-defect
Loss = proportion out of specification × total number × cost of product
Standard normal variable at LSL
At USL
Z 1 = 16 - 18/ 0.66
= - 3.03
Z2 = 24 - 18/0.66 = 9.09
∴ Proportion out of specification from tables,
= F (- 3.03) + F (9.09)
= 0.00122 + 0
= 0.00122
∴ Loss = 0.00122 × 100000 × 100
= 0.122 × 105 Rs.
Loss-by-dispersion
Loss = Loss per piece × Number of products
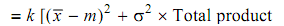
k = A/ Δ2
= 100 = 6.25
∴ Loss = 6.25 [(18 - 20)2 + 0.662] × 1,00,000
= 27.7 × 105
Process III
x = 17, σ = 0.40
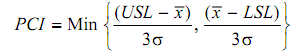
= Min {24 - 17/3 ´0.4 , 17 - 16 /3´0.4}
= min {5.83, 0.83}
∴ PCI = 0.83
At LSL Z = 16 - 17 /0.4 = - 2.5
At USL Z = 24 - 17 /0.4 = 17.5
∴ Proportion out of specification, from tables
= F (- 2.5) + F (17.5)
= - F (2.5) + F (17.5)
= 0.00621 + 0
= 0.00621
∴ Loss by defect = Proportion out of specification × Total product
× Cost of product
= 0.00621 × 100000 × 100
= 0.621 × 105
Loss-by-dispersion
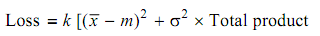
= 6.25 [(17 - 20)2 + 0.42] × 100000
= 57.25 × 105