1. Beta catenin is a protein that translocates to the nucleus in the presence of Wnt ligand. In the absence of Wnt, beta catenin is targeted for degradation. Using a cell line from a new species of frog, Xenopus simulatus, you have found a protein that you believe is homologous to beta catenin, as it translocate to the nucleus in the presence of Wnt, but does not appear to be degraded in the absence of Wnt. You call this protein Better catenin.
You're interested in determining which regions of Better catenin are responsible for its localization within the cell. You generate deletion mutants of each of Better catenin's 5 regions (shown below), all fused to GFP. You express each construct in your cell line and examine the localization of Better catenin in the presence and absence of Wnt (Table 1). In both charts below, Δ stands for "deletion", so only the ΔX portion of the protein is missing.
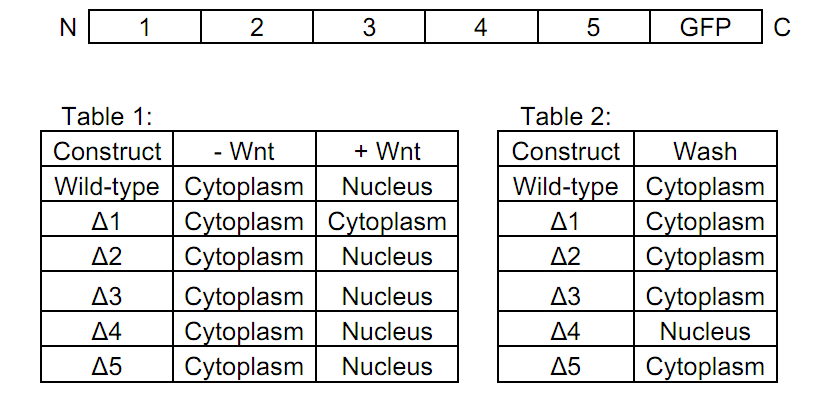
A) Which region of Better catenin is necessary for nuclear import, and what does this region contain?
B) In a second experiment, you express your deletion mutants in cells that are exposed to Wnt. After 30 minutes you wash Wnt away from the cells and observe the cellular localization of Better catenin. Your results are summarized in Table 2. What is your interpretation of these results?
C) Finally, using your wild-type GFP-tagged protein, you examine Better catenin localization in a cell line that has a non-functional Ran-GEF. Predict what would happen to Better catenin in the absence and presence of Wnt, and when Wnt is washed away as before, and describe where you would see GFP.