C compiler does not verify the bounds of arrays. It is your job to do the essential work for checking boundaries wherever required.
One of the most common arrays is a string that is simply an array of characters finished by a null character. The value of any null character is o. A string constant is a one-dimensional array of characters terminated by a null character (\0).
For instance, consider the following:
char message[ ]= {'e', 'x', 'a', 'm', 'p', 'l','e','\0'};
Also, assume the following string that is stored in an array:
"sentence\n"
Given figure illustrates the way a character array is stored in memory. In the array each of character occupies one byte of memory and the last character is always '\0'. Note down that '\0' and '0' are not the same. The character array elements are stored up in contiguous memory locations.
Figure: String in Memory
C concedes a fact that the user would employ strings very frequently and therefore provides a short cut for initialization of strings.
For instance, the string used above can also be initialized as char name[ ] = "sentence\n";
Note down that, in this declaration '\0' is not essential. C automatically inserts the null character.
Multidimensional arrays are described in the similar manner as one-dimensional arrays, apart from that a separate pair of square brackets is needed for each of subscript. Therefore a two-dimensional array will need two pairs of square brackets, a three-dimensional array will need three pairs of square brackets and so on.
In C the format of declaration of multidimensional array is given below:
data_type array_name [expr 1] [expr 2] .... [expr n];
where data_type is the type of array like char, int etc., array_name is the name of array & expr 1, expr 2, ....expr n are positive valued integer expressions.
The diagram of two-dimensional array of size 3 × 5 is illustrated in Figure
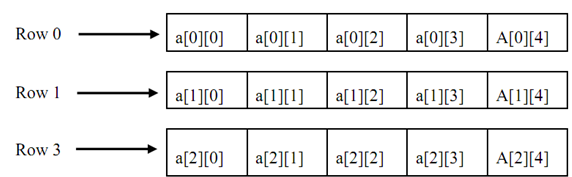
Figure: Schematic of a Two-Dimensional Array
In the particular case of a two-dimensional array, the given formula yields the number of bytes of memory required to hold it:
bytes = size of 1st index × size of 2nd index × size of (base type)
The pointers & arrays are closely associated. As you know, an array name without an index is a pointer to the primary element in the array.
Assume the following array:
char p[10];
p and &p[0] are similar because the address of the primary element of an array is the similar as the address of the array. Thus, an array name without an index produced a pointer. On the other hand a pointer can be indexed as if it were declared to be an array.
For instance, assume the following program fragment:
int *x, a [10];
x = a;
x[5] = 100;
* (x+5) = 100;
Both of the assignment statements place the 100 in the sixth element of a. In addition the (0,4) element of a two-dimensional array might be referenced in the given two ways: either through array indexing a[0][4], or through the pointer *((int *) a+4).
Generally, for any two-dimensional array a[j][k] is equivalent to:
*((base type *)a + (j * rowlength)*k)