Reference no: EM131273723
Ecnomics: Problem Set
Always show the calculations leading to your final answer. Question 1) Consider the following extensive form:
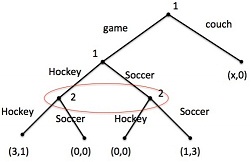
Figure 1:
a) Find all subgame perfect equilibria of this extensive form. How do they depend on x?
b) For which values of x can we use the concept of forward induction to rule out all but one subgame perfect equilibrium?
Question 2) Consider the (corrected!) card game considered in class:
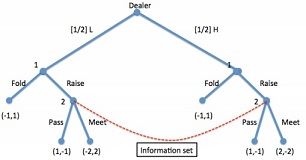
Figure 2: Card game
a) Find all subgame perfect equilibria of this game.
b) Now suppose player 2 has found a way of cheating, getting to observe player 1's hand (the cheating is common knowledge). Represent the extensive form of this game and find its subgame perfect equilibria.
Question 3) Consider the following extensive form, where two friends decide what to do on a weekend but with limited ability to communicate:
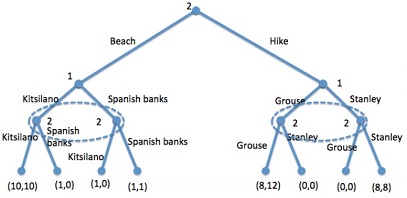
Figure 3:
a) What is the minimum player 2 can obtain if she chooses "hike" and then randomizes between "Grouse" and "Stanley" with equal probabilities? This is a lower bound for the payoff that can be obtained from choosing "hike".
b) Using the concept of forward induction and the result in (a), what should player 1 think following the decision by player 2 to go to the beach? What should then player 1 chooses after observing "Beach"?
c) Using the answers in (a) and (b), what should player 2 do if she indeed decides to go to a beach? Which payoffs than should be assigned to both players to the subgame following "beach"?
d) Now, using the answer in (c). What should player 1 expect player 2 to do following "hike"? In response, what should player 1 do following "hike"?
e) Using what we've learned in (a)-(e), what should be the decision by player 2 in the initial node? Describe a subgame perfect equilibrium consistent with forward induction.
f) Construct a subgame perfect equilibrium inconsistent with the forward induction arguments put forth in (a)-(e).
For the next three questions, consider the following extension of the bargaining model discussed in class. Three participants, names 1, 2 and 3, need to divide a prizer of total size 1. An offer of division is (x1, x2, x3), where xi represents the share of the prize that player i keeps. Offers must satisfy x1 + x2 + x3 = 1. We will consider different protocols where, in each round, one of the players makes an offer that is either accepted or not by one other player. All three players discount payments with equal discount factor 6 2 (0, 1).
Question 4) Consider the following protocol with three offers.
1. Player 1 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 2.
2. Player 2 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 3.
3. Player 3 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 1.
If any of the offers is accepted, the game is over and each part receives what is mandated by the agreed upon offer. If none of the first three offers is accepted, all players get a payoff of zero.
a) Write down the extensive form of this game.
b) Find a subgame perfect equilibrium of this game.
Question 5) Now consider the following infinite horizon bargaining procedure.
1. Player 1 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 2.
2. If the last offer is not accepted player 2 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 3.
3. If the last offer is not accepted player 3 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 1.
4. Step 1 is repeated
5. Step 2 is repeated
6. Step 3 is repeated...
In summary, as long as offers are not accepted, player 1 gets to make an offers in each period 3k, for k = 1, 2, ...; player 2 makes offers in periods 3k + 1, for k = 1, 2, ...; and player 3 makes offers in periods 3k + 2, for k = 1, 2, ...
a) Find a stationary symmetric subgame perfect equilibrium of this model in which (you can assume that offers made in equilibrium are accepted and that receivers accepted offers when indifferent):
• the offering player always asks to keep x? to him/herself,
• the receiving player always accepts offers that give him/herself at least x.
Hint: If player 1 is making an offer to player 2, there isn't much incentive to be generous to player 3. The same is true for any other combination.
b) What is the equilibrium outcome? What is the division of the prize among the three players?
Question 6) Now consider the following modification of the protocol described in question 5:
1. Player 1 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 2.
2. If the last offer is not accepted player 3 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 1.
3. If the last offer is not accepted player 2 makes an offer, which is accepted (or not) by player 3.
4. Step 1 is repeated
5. Step 2 is repeated
6. Step 3 is repeated...
a) Find a stationary symmetric subgame perfect equilibrium of this model in which (you can assume that offers made in equilibrium are accepted and that receivers accepted offers when indifferent):
• the offering player always asks to keep x? to him/herself,
• the receiving player always accepts offers that give him/herself at least x.
Hint: If player 1 is making an offer to player 2, there isn't much incentive to be generous to player 3. The same is true for any other combination.
b) What is the equilibrium outcome? What is the division of the prize among the three players?
Question 7) Two players interact playing the following stage game:
|
|
l
|
m
|
r
|
|
U
|
-1,0
|
0,0
|
1,1
|
|
M
|
2,2
|
8,0
|
0,-1
|
|
D
|
0,9
|
7,7
|
0,0
|
Table 1:
a) Find all Nash equilibria of this normal form (hint: could actions D and m be played in a Nash Equilibrium).
b) Suppose this game is repeated for 2 periods, with the second period payoff being discounted by 6 2 (0, 1) by both players. Is there an action profile in which both players are better off than in any NE found in (a)? Can you find a subgame perfect equilibrium of the repeated game in which this action profile is played in the first period? If so, describe the conditions on 6 and the SPE.
c) Now suppose this game is repeated infinitely (with discounting 6 2 (0, 1)). Find the minimum discount factor 6 such that the action profile discussed in (b) is played in every period (on-path) as part of a subgame perfect equilibrium (Hint: the easiest way to sustain cooperation is by using the most extreme punishment. What is this punishment for this stage game?). Fully describe what is the SPE that sustains this equilibrium play.