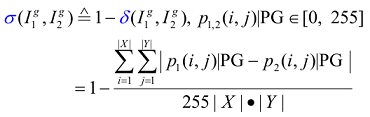Reference no: EM132500692
Computer Vision Assignment -
Question 1 - Multiple choice questions on key principles, basic concepts, fundamental theories, and useful algorithms.
1. Computer vision studies ma ny of the following topics except:
a. Image representations
b. Mathematical models and algorithms for image processing
c. Engineering graphics
d. Computational arts
2. What is the usage of the following algorithm: ImG = 0.30r + 0.59g + 0.11b, given a true color image (ImC), its (r, g, b) components, and the corresponding gr ay scale image (ImG)?
a. The core algorithm of the MATLAB function ImG = rgb2gray(ImC)
b. An instance where ImG = ImC
c. An algorithm for transferring ImG into ImC
d. A normalization of ImC onto ImG
3. What is the typical backgrounds ubtraction technologies for object detection and location in the following list except:
a. Frame differentiation
b. Shadow detection
c. Dark threshold
d. Contour extraction
4. The conditions of equivalency for image convolution and correlation are as follows except:
a. The mask is x and y symmetric
b. The mask is a disk
c. The mask is an all one matrix
d. The mask is pre-mirrored for convolution
5. The big-R notation (as shown in Question V) may be used to denote the following list of algorithmic specifications for computer vision except:
a. Code implementations
b. Recurring structural entities (data structures)
c. Repetitive software behaviors (functions)
d. Iterations and recursions
6. In case you need to remove small dots, short lines, and/or fine holes in an image/frame for object recognition, what are the methodologies that you may adopt in the following except:
a. Morphological operations
b. Filter operations
c. Neighborhood operations
d. Geometrical operations
7. What is the normal process for object recognition in images given the following tools/technologies: (1) Boundary recognition; (2) Region feature analysis; (3) Region labeling; and (4) Region property detection?
a. 1-2-3-4
b. 4-3-2-1
c. 1-3-4-2
d. 2-1-4-3
8. The usage of filters in image restoration may be classified in the following categories except:
a. Winner Band-Reject Filters (BRF)
b. LPF for image deblurring
c. HPF for image sharpening
d. Image filters in both spatial and frequency domains
9. Computer vison covers several categories of image processing technologies as partially given below. Try to provide an additional category of technologies in (e):
a. Mathematical/logical operations
b. Geometrical/morphological operations
c. Neighborhood (mask) operations
d. Filtering operations
e. ________________________
10. Computer vison has found a wide range of industrial applications underpinned by AI and machine learning technologies. May you provide one of the application domains in addition to the following list?
a. Image pattern recognitions
b. Self-driving cars
c. Intelligent robots
d. Unmanned systems
e. ________________________
Question 2 - Color space representation and transformation in computer vision are fundamental technologies for image processing. Try to provide suitable methods or equivalent built-in functions of MATLAB for each of the directed links between a pair of color images in the following color framework.
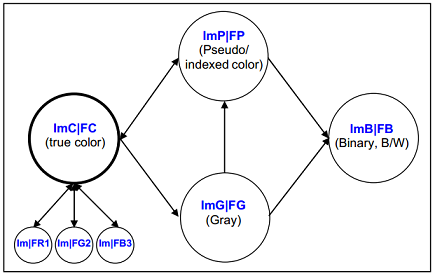
Then, analyze what are the necessary and sufficient color information (scheme) for enabling seamlessly transformations and regenerations among all color schemes.
Question 3 - Manipulations of bounding boxes (Bboxes) are a key technology for objects detection and recognition based on machine learning. Given an initial set of Bbox3[x, y, w, h] with three elements (objects) in a target image frame ImC, determine the following factors and outcomes by a formal expression or equivalent MATLAB functions.
a. How do you determine the size (Sb3) of Bbox3?
b. How would you insert an additional bounding box into Bbox3 by a hard-coded item given as bbox = [10, 200, 30, 50]?
c. Suppose the newly inserted object in Bbox4 is identified by Obj4 as the image of an object. How can Obj4 be composed into the original frame ImC?
d. Try to extract the second image (Im2) in Bbox4 as located by the corresponding bounding box.
Question 4 - In the experiment of Lab 5, you've observed that current deep machine learning technologies for computer vision cannot recognize faces in an arbitrary image frame Im|f = i=1Rnj=1RmIm(i, j)|P, if it is upside down.
a. What is/are your solution(s) to solve this problem mimicking human cognition?
b. If you'd prescreening a given image in order to detect if an image frame is upside down before applying the neural-network-based facial detection system, you will need to create a 180o rotated image Im'|F. How will this action be formally expressed in the algorithm given Im|f = i=1Rnj=1RmIm(i, j)|P?
c. Try to prove or formally de scribe that the similarity measure, σ(I1g, I2g), between Im|F and Im'|F will result in an inconsistency detection, i.e., δ(I1g, I2g) > 0, where