Systems of Equations Revisited
We require doing a quick revisit of systems of equations. Let's establish with a general system of equations.
a11 x1 + a12 x2 +................+a1n xn = b1
a21 x1 + a22 x2 +.............. +a2n xn = b2
...................
an1 x1 + an2 x2 +............... +ann xn = bn ...................(1)
Here, covert each side in a vector to find,
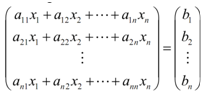
The left side of such equation can be thought of like a matrix multiplication.
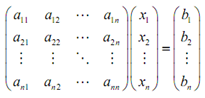
Simplifying up the notation a little provides,
A x? = b? ................................(2)
Now there, x? is a vector that elements are the unknowns in the original system of equations.
We take (2) the matrix form of the system of equations (1) and resolving (2) is equal to solving
(1). the solving process is identical. The augmented matrix for (2) is,
A(b?)
Once we contain the augmented matrix we proceed as we did along with a system which hasn't been wrote in matrix form.
We also have the subsequent fact regarding to solutions to (2).
Fact
Provided the system of equation (2) we contain one of the subsequent three possibilities for solutions.
1. There will be no more solutions.
2. There will be particularly one solution.
3. There will be infinitely various solutions.
Actually we can go a little farther here. Because we are assuming that we've got similar number of equations like unknowns the matrix A in (2) is a square matrix and therefore we can calculate its determinant. This provides the following fact.
Fact
Provided the system of equations in (2) we have the subsequent.
1. If A is nonsingular then there will be particularly one solution to the system.
2. If A is singular then there will either be no solution or infinitely various solutions to the system.
The matrix form of a homogeneous system is as,
A x?= 0?
Here 0? is the vector of all zeroes. Under the homogeneous system we are guaranteed to have a solutions, x? = 0?. The fact above for homogeneous systems is so, Fact
Given the homogeneous system (3) we contain the subsequent.
1. If A is nonsingular then the only solution will be x? = 0?
2. If A is singular then there will be infinitely many nonzero solutions to the system.