Magnitude, direction and position of resultant force:
Q : A horizontal line PQRS is 12 m long, and PQ = QR = RS = 4m. Forces of 1000, 1500, 1000 and 500 N act at P, Q, R and S in that order with downward direction. Their lines of action make angle of 90º, 60º, 45º and 30º in that order with PS. Find out the magnitude, direction and position of resultant force.
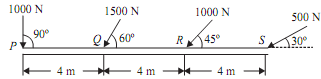
The system of given forces is shown in the figure given below
Let R be resultant of given system. And RH and RV be horizontal and vertical component of resultant.
By resolving all the forces horizontally
∑H = -1000 cos 90º - 1500 cos 60º - 1000 cos 45º - 500 cos 30º
∑H = -1890 N ...(i)
By resolving all the forces vertically
∑V = -1000 sin 90º - 1500 sin 60º - 1000 sin 45º - 500 sin 30º
∑V = -3256N ...(ii)
As, R = (∑H)2 +(∑V)2
R = (1890)2 + (3256)2
R = 3764N .......ANS
Let θ = Angle makes by the resultant
tanθ = ∑V/ ∑H = 3256/1890 θ= 59.86º
For position of resultant
Let, d = Distance between P and line of action of resultant force. Apply the varignon's theorem
R.d = 1000 sin 90º × 0 + 1500 sin 60º × 4 + 1000 sin 45º × 8 + 500 sin 30º × 12
3256.d = 13852
d = 3.67 m .......ANS