Important Points about the Curve segment - properties of bezier curves
Note: if P (u) → = Bezier curve of sequence n and Q (u) → Bezier curve of sequence m.
After that Continuities in between P(u) and Q(u) are as:
1) Positional continuity of 2 curves
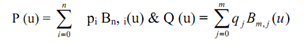
That is pn = q0
2) C1 continuity of 2 curve P (u) and Q (u) as that point pn - 1, pn on curve P(u) and q0, q1 points upon curve Q(u) are collinear that is:
n( pn - pn-1 ) = m(q1 - q0 )
n q1 = q0 +( pn - pn -1 ).(n/m)
⇒ (d p/du)u=1 = (d q/dv)v=0
G(1) continuity of two curves P(u) and Q(u) at the joining that are the end of P(u) along with the beginning of q(u) as:
pn = q0n( pn - pn -1 ) = kn(q1 - q0 ),
Here k is a constant and k > 0
⇒ pn -1 , p = q0 , q1 are collinear
3) c2 continuity is:
a) C(1) continuity
b) m (m - 1) (q0 - 2q1 + q2)
= n (n - 1) (pn - 2pn - 1 + pn - 2)
That points are as: pn - 2, pn - 1, pn of P(u) and points q0 , q1, q2 of Q(u) should be collinear further we can verify whether both second and first order derivatives of two curve sections are similar at the intersection or not that is:
(d p)/( d u) u=1 = (d q) /(d v )v=0
And (d2 p)/( d u2) u=1 = (d2 q) /(d v2 )v=0
Whether they are similar we can as we have C2 continuity
Note: as the same we can explain higher order parametric continuities