Like general tree, binary trees are implemented through linked lists. A typical node in a Binary tree has a structure as follows
struct NODE
{
struct NODE *leftchild;
int nodevalue; /* this can be of any data type */
struct NODE *rightchild;
};
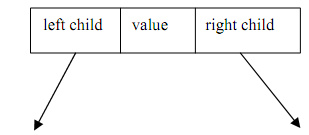
Figure: Node structure of a binary tree
The 'left child 'and 'right child' are pointers to another tree-node. The "leaf node" (not shown) here will have NULL values for these pointers.
The binary tree creation follows a extremely simple principle. For the new element to be inserted, compare it along with the current element in the tree. If its value is less than the present element in the tree, then move to the left side of that element or else to its right. If there is no sub tree at the left, then make your new element as the left child of that present element or else compare it to the existing left child and follow the similar rule. Exactly, the same need to done for the case while your new element is greater than the current element into the tree however this time with the right child. Though this logic is followed for the formation of a Binary tree, this logic is frequently suitable to search for a key value in the binary tree.
Following is algorithm for the implementation of Binary tree:
Step-1: If new element < current element, then go to step-2 or else go to step -3
Step-2: If the current element does not contain a left sub-tree, then converts new element into the left child of the current element; else make the existing left child as your current element and go to step-1
Step-3: If the current element does not contain a right sub-tree, then converts new element into the right child of the present element; else make the existing right child as your existing element and go to step-1