Reference no: EM131708364
Differential Equation
1. If y1 (x), y2 (x)are solution of y" + xy' + (1-x2)y = sin x, then which of the following is also its solution:..................
(a) y1 (x) + y2 (x) (b) y1 (x) - y2 (x) (c) 2y1 (x) - y2 (x) (d) y1 (x) - 2y2 (x)
2. The differential equation dy/dx+py = Q are function of x only, have integrating factor
(a) efPdx (b) efQdy (c) efPdy (d) efQdx
3. The differential equation whose linearly independent solutions are cos 2x, sin 2x, and e-xis:.........................
(a) (D3 + D2 + 4D) y= 0 (b) (D3 - D2 + 4D - 4) y= 0 (c) (D3 + D2 -- 4D - 4) y= 0 (d) N.O.T
4. The differential equation dy/dx = k (a - y) (b - y) when solved with the condition y (0) = 0, fields the result..................
(a) (b (a-y))/(b (b-y)) = e(a-b)kx (b) (a (b-y))/(b (a-y)) = e(a- b)kx (c) (b (a-x))/(a (b-x)) = e(b- a)kx (d) xy = kc
5. The solution of (x+1) dy/dx = 1- e-y is.................
(a) (x + 1) ey = x + c (b) (x + 1) (1+ey ) = c (c) (x+1)/1+ex = c (d) (x+1)/1+ey = c
6. (D+1) x + (D-1)y = et (D2 + D + 1)x + (D2 - D + 1)y = t2, where D = d/dt:........
(a) y = 1/3 (3t + t2 - 2et) (b) y = 1/4 (2t + t3 - 3et) (c) y = 1/2 (2t + t2 - 2et) (d) y = 1/2 (2t + t2 - 3et)
7. Integrating factor of DE (y2 + 2x2y) dx + (2x3 - xy) dy = 0 is............................................
(a) x1/2 y-5/2 (b) x3/2/y5/2 (c) x-5/2 y-1/2 (d) x-5/2 y-5/2
8. If eax 4 (x) is a PI of d2y/dx2 - 2a dy/dx + a2y = f (x), where a is a constant, then (d2y)/dx2 is equal to:...
(a) f (x) (b) f(x) eax (c) f(x) e-ax (d) f(x) (eax + e-ax)
9. Any equal contains n-arbitrary constants, then the order of differential equation derived form it is : .............................................
(a) n (b) n-1 (c) 2 (d) n+1
10. The solution fo differential equation y' sin x = y log y satisfying initials condition y (Π/2) e is:......................
(a) etan x/2 (b) ecot x/2 (c) log tan (x/2) (d) log cot (x/2)
11. Let y = ex be a solution of x (d2y/dx2 - dy/dx + (1- x) y = 0, then the second linerarly independent solution of this ODE is:................
(a) xe-x + 1/2 (b) 1/2 (x- 1/2) e-x (c) - 1/2 (x+1/2) (d) xe-x - 1/2
12. Let y be function of x satisfying dy/dx = 2 x3√y - 4xy of y (0) = 0 then y (1) is:...................
(a) 1/4e2 (b) 1/e (c) e1/2 (d) e3/2
13. The IF of DE (2x y4 ey + 2xy3 + y) dx + (x2 y4 ey - x2 y2 - 3x)dy = 0:..........................................
(a) 1/x4 (b) y2/x4 (c) 1/y4 (d) N.O.T
14. Particular integral of the following differential equation (D2 - 4D +4) y = (e2x log x)/x PS obtain by integrating
(a) (x log x)/2 (b) (x(log x)2/2 (c) (log x)2/2 (d) ((x logx)2)/2
15. The solution of the differential equation xdy - ydx = √(x2 + y2 ) dx is :...............................
(a) y + √(x2 + y2 ) = xc (b) y + √(x2+ y2 ) = x2c (c) y -√(x2+ y2 ) = xc2 (d) N.O.T
16. If y1 and y2 are two solutions of y" + p (x) y' + q (x) y = 0, then general solution of this equation y1and y2 are :........
(a) Linearly dependent (b) linearly independent (c) proportional
17. The solution of the differential equation (x3 y3 + xy) dy/dx = ? is:.............................................
(a) 1/x = 2-y2/2 + Aey2/2 (b) x = 2 - y2 + Aey2/2 (c) 1/x = 2-y2 + Ae-y2/2 (d) N.O.T
18. Solution of (d2y/dx2 - 2/x dy/dx + (1+2/x2 )y = xex is
(a) y = x (c1 cos x + c2 log x + 1/2ex)
(b) y = x (c1 cos x + c2 sin x )
(c) y = - x (c1 cos x + c2 sin x )
(d) y = x (c1 cos x + c2 sin x + 1/2ex)
19. Solution of DE (d2y)/dx2 + y = cosec x is
(a) y = c1 cos x + c2 sin x - x cos x + sin x log sin x
(b) y = c1 sin x + c2 cos x - x sin x + sin x log cos x
(c) y = c1 cos x + c2 sin x-x sin x + cos x log sinx (d) N.O.T
20. A function f (t) = d/dt {dx/(1-cos t cos x)}satisfies the differential equation :................................
(a) dt/dt + 2f (t) cos t = 0 (b) dt/dt - 2f (t) cos t = 0 (c) dt/dt + 2f (t) sin t = 0 (d) dt/dt - 2f (t)sin t = 0
21. Solution of (d2y)/dx2 + cot x dy/dx + 4y cosec2x= 0 is:........
(a) y = k1 cos (2 log tan x/2 + k2 )
(b) y = k1 sin ( log tan x/2 + k2 )
(c) y = k1 cos ( log tan x/2- k2 )
(d) y = k1 cos (-log tan x/2 + k2 )
22. Given, an equation (d3y)/dx3 + d2y/dx2 + 4 dy/dx + 4 = 0. Has solution:....................................................
(a) y = c1e-x + xc2 e-x + x2 c3e-x
(b) y = c1 cos 2x + c2 sin 2x
(c) y = c1e-x + c2 sin 2x + c3 sin 2x (d) N.O.T
23. The integrating factor for the differential equation (x + 1) dy/dx - y = e3x (x + 1)2 is:............
(a) 1/(x+1) (b) x + 1 (c) 1/(x2+1) (d) x2+1
24. The solution of the differential equation x {y (d2y/dx2 +(dy/dx)2 } + y dy/dx = 0 , is :........................
(a) ax + by = c (b) ax2 + by = 0 (c) ax2 + by2 = 0 (d) ax + by2 = 0
25. If y' - x ≠ 0, a solution of differential equation y' (y'+y) = x (x + y) is given if y(0) = 0
(a) 1 - x - e-x (b) 1- x +ex (c) 1+ x +e-x (d) 1+ x +ex
26. The solution of the differential equation (cos x - sin x) (d2y)/dx2 + 2sin x dy/dx - (cos x + sin x) y = 0, given that y = sin x is a solution, is :..........
(a) c1 cos x + c2 x sin x (b) c1 sin x + c2 x sin x (c) c1 sin x + c2 ex (d) ) c1 sin x + c2x
27. LetΦ1(x) and Φ2(x) are particular integral of L(y) = eaxf(x)a, b being constants, then a PI of L(y) = 2 beax is:..............
(a) bΦ1(x) + Φ2(x) (b) Φ1(x) - bΦ2(x) (c) aΦ1(x) + bΦ2(x) (d) b[Φ1(x) + Φ2(x)]
28. The particular solution of (d3y)/dx3 + y = cos (2x - 1) is:.........................
(a) 1/65 [cos (2x - 1) - 8] (b) 1/65 [cos (2x - 1) - 8 sin (2x - 1)] (c) 1/65 [cos (2x + 1) + 8] (d) N.O.T
29. Let W [y1 (x), y2 (x)] is the wonkier formed for the solution y1 (x) and y2 (x) of the differential equation y" + a1 y'+ a2y = 0, if W ≠ 0 for same x = x0 in [a, b], then:..................
(a) It vanishes for any x ∈ [a, b]
(b) it does not vanish for any x ∈ [a, b]
(c) If does not vanish only at x = a
(d) If does not vanish only at x = b
30. If k is any constant such that xy + k = e ((x-1)2)/2 satisfies the differential equation x dy/dx = (x2 - x - 1) y + (x - 1) then k is equal to :.......
(a) 1 (b) 0 (c) -1 (d) -2
31. All non- trivial solution of x2 y" + xy' + 4xy = 0, x > 0 are:....................................................
(a) bounded and non- periodic
(b) unbounded and non periodic
(c) bounded periodic
(d) unbounded and periodic
32. Ly= xex log x [x > 0], when L = (d2/dx2 + P.d/dx + Q) the two LI solution of Ly = 0, are xex and ex, then PI is:........
(a) xex[x/2 log (x-x)2/x] + e-x [-x3/3 log x3/a]
(b) x2ex [x2/2 log (x-x)2/x] + ex [-x2/2 log (x + x3)/a]
(c) x2ex[x2/2 log (x-x)2/x] + ex[-x3/3 log (x + x3)/a].............
(d) N.O.T
33. The solution of y" + ay' + by = 0. Where and b are constants, approaches to zero as x →∞ then:.........
(a) a > 0, b > 0 (b) a > 0, b < 0 (c) a < 0, b < 0 (d) a < 0, b > 0
34. Differential equation |y'|+|y| = has.....................................
(a) G S solution
(b) G S solution but no arbitrary constant
(c) Particular solution which is bounded
(d) N.O.T
35. The ordinary differential equation x dy/dx - y = = 2x2 with initial condition y (0) = 0, has:.....
(a) no solution (b) a unique solution (c) two district solution (d) Infinitely many solutions
36. Let y1 (x) and y2 (x) be two linearly independent solution at the differential equation x (d2y)/dx2 - 2x2 dy/dx + exy = 0 satisfying y1 (0) = 1 y2 (0) = - 1 y1' (0) = 1 and y2' (0) = 1, then the wronskian of y1 (x) and y2 (x) at x = 2............ w|y1 y2 | x = ?equal to:...............
(a) 2e-1 (b) 2e2 (c) 2e4 (d) 2e-4
37. Let y (x) be 0 non-trivial solution of the 2nd order linear differential equation (d2 y)/dx2 + 2c dy/dx + ky = 0, where c < 0, k > 0 and c2 > k, then
(a) |y(x)|→∞ as →∞(b) |y(x)|→0 as →∞ (c) (x→lim )±∞ |y(x)| exists and is finit(d) N.O.T
38. If y1 (x) and y2 (x) are solution of y" + x2y' - (1- x) y = 0 such that y1 (0) = 0, y1' (0) = - 1 and y2(0) = - 1, y2' (0) = 1, the wronskian w (y1, y2) on R:.......................................................
(a) is never zero (b) is identically
(c) is zero only finite member of points
(d) is zero at countable infinite member of points
39. Let y1 and y2 be two linearly independent solutions of y" + (sin x) y = 0, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 Let g (x) = w (y1, y2) (x) be the Wronskian of y1 and y2. Then:................................................................
(a) g' > 0 on (0, 1) (b) g' < 0 on (0, 1)
(c) g' vanishes at any one point
(d) g' vanishes at all points of (0, 1)
40. The Largest value of c such that there exists a function h (x) for - c < x < c that is a solution dy/dx = 1 + y2 with h (0) = 0 is given by
(a)Π/3 (b) Π/2 (c) Π/4 (d)Π
41. If 2x (1 - y) = k and g (x, y) = L are orthogonal families of curves where K and L constant then g (x, y) is
(a) x2 + 2y - y2 (b) 2 {y +2 [y + (1- x)] (c) x2 + 2x - y2 (d) x2 - 2y +y2
42. If y1 (x) = x and y2 (x) = xex are two linearly independent solutions of x2 (d2y)/dx2 - x (x + 2)dy/dx + ( x+ 2)y = 0, then the interval on which they form a fundamental set of solution is:.............
(a) x > 0 or x < 0 (b) -1 < x < ∞ (c) -1 < x < z (d) - ∞ < x < ∞
43. The solution of the differential equation y dy/dx + (1 + y2) sin x = 0 y (0) = 0, exists in the open interval (-a,a), then a is equal to :.......
(a) 2 cos-1 (1/2 √log2) (b) 2 tan-1(1/2 √log2) (c) 2 sin-1 (1/2 √log2) (d) 2 cot-1 (1/2 √log2)
44. For non-homogeneous equation y'+ P(x) y = r(x), if y1 an d y2 are its solution, then the solution is homogenous equation y' + P (x) y = 0 is:..................
(a) y = y1 - y2 (b) y = y1/y2 (c) y = y2/y1 (d) N.O.T
45. Solve dy/dt = √(|y| ), for 0 <y < 10 and y (0) = 0
(a) has unique solution (b) has no solution
(c) has two independent solution
(d) has infinite solution
46. The general solution dy/dx + y = f (x), where
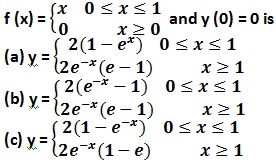
(d) N.O.T
47. For (d2y)/dx2 + 4y = tan 2x solving by vacation of parameter the value of wronskian W is:...
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
48. Let a, b∈ R, let y = (y1, y2 ) T be a solution of the system equation y11 = y21, y2 = ay1 + by2 every solution (x) → 0 as n → ∞ if :............
(a) a < 0, b < 0 (b) a > 0, b>0 (c) a> 0, b > 0 (d) a > 0, b >0
49. Suppose yp (x) = x cos 2 (x) is a particular solution y" + αy = - 4 sin 2x, then the constant α equals:..............................................
(a) - 4 (b) - 2 (c) 2 (d) 4
50. The value of wronksion W (x, x2, x3) is:......
(a)2x4 (b) 2x2 (c) 2x3 (d) N.O.T
51. Which of the following transformation reduce the differential equation dz/dx + z/x log z = z/x (log z)2 into the form du/dx + P (x) ..
(a) u = log z (b) u = 1/(log z) (c) u = ez (d) u = (logz)z
52. If (c1 + c2 log x)/x is the general solution of the differential equation x2 d2y/dx2 + kx dy/dx + y = 0, x > 0 then k equals:......
(a) 3 (b) - 3 (c) 2 (d) - 1
53. Consider the differential equation dy/dx = ay - by2 where a, b > 0, and y (0) = y0 as x → ∞, the solution y (x) finds to:.......
(a) 0 (b) a/b (c) b/a (d) y0
54. If g (x, y) dx + (x + y) dy = 0 is an exact differential equation and if g (x, 0) = x2, then the general solution of the differential equation is :....
(a) 2x3 + 2xy + y2 = c (b) 2x3 + 6xy + 3y2 = c (c) 2x + 2xy + y2 = c (d) x2 + 2xy + y2 = c
55. Let f1 g: [- 1, 1] → R, f (x) = x3, g (x) = x2 |x|. Then:......
(a) f and y are linearly independent on [ -1, 1]
(b) f and y are linearly dependent on [ -1, 1]
(c) f (x) g' (x) - f' (x) g (x) is not identical zero on [ - 1, 1]
(d) Then exists continuous function p (x) and g (x) such that
56. Let k be a real constant. The solution of the differential equation dy/dx = 2y + z and dz/dx = 3y satisfies the relation :..........
(a) y - z = ke3z (b) y + z = ke-x (c) 3y + z = ke3z (d) 3y + z = ke-3x
57. Let y' (x) + y (x) g' (x) = g (x) g'(x) if y (0) = 0 & g(0) = 0, then f (2) = ?
(a) 0 (b) 3 (c) 5 (d) N.O.T
58. Let f : [1, ∞] →[2, ∞] be a differentiable function such that f (1) = 2, 6 1∫xf (t). dt = 3x f (x) - x3 for all x ≥ 1, then the value of f(z):...
(a) 8 (b) 6 (c) 3 (d) N.O.T
59. If x = 1 + dy/dx + 1/L2 (dy/dx)2 +1/L3 (dy/dx)3 +.......+ 1/Ln (dy/dx)n+......., degree of differential equation
(a) not define (b) n (c) 1 (d) N.O.T
60. The O. T. of the circle x2 + y2 - ay = 0 if y (1), where a is parameter.
(a) x2 + y2 = cx (b) x2 + y2 = 2cx (c) x2 + y2 = c (d) x2 + y2 = cx
61. The particular solution of the differential equation y" + y' + 3y = 5 cos (2x + 3) is:............
(a) 2 cos (2x + 3) - sin (2x + 3) and two absolute constant. (b) 2 sin (2x + 3) - cos (2x + 3) (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
62. If n is a positive integral value of the 1/((D-α)) . eαx:.........
(a)xn/L(n+1) eαx (b) 1/Ln eαx (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
63. According to E. C. E the P. I if (x2 D2 + 3xD +1) y = 1/(1-x)2 :......................
(a) (c1 + c2 log x) x-1 (b) x-1 log {x|(1-x)} (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
64. Solve (x2 + y2 + x)dx - (2x2 + 2y2 - y) dy = 0
(a) x - 2y + 3/2 log (x2 + y2) = c (b) x - 2y + 1/2 log (x2 + y2) = c (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
65. If (D4 + m4) y = 0 then the solution of the equation:..........
(a) mei Π/4 (b) m (c) me5i Π/4 (d) m e7i Π/4
66. The solution of D. E (d2y)/dx2- y = 1 which vanishes when x = 0 and tends to a finite limit as x→∞:..
(a) y = e2x-1 (b) y = ex-1 (c) y = ex (d) N.O.T
67. The set of eigen vectors x1,x2,......., xn corresponding to distinct eigen vectors λ1,λ2,.....λn then square of matrix
(a) singular (b) L.D (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
68. If A is any non-singular square matrix and |A| = 5 and order of A is 4 then determinant of adj (adjA) = ?
(a) 1.9 × 106 (b) 5.9 (c) 3220 (d) N.O.T
69. If K is any scalar then adj (K In):..................
(a) Kn-2 In (b) K adj In (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T
70. Let Abe a 3x3 matrix with trace (A) = 3, and det (A) = 2. If 1 is Eigen vector, then other two eigen values:...................................
(a) 1+ I (b) 1- I (c) (a) & (b) (d) N.O.T