Q. With the help of a npn transistor circuit and wave forms explain the working of an astable multivibrator
In astable multivibrator both transistors are coupled to each other through capacitors as shown in the circuit diagram. Whichever transistor is off at any moment cannot remain off indefinitely; its base will become forward biased as that capacitor charges towards +5 volts.
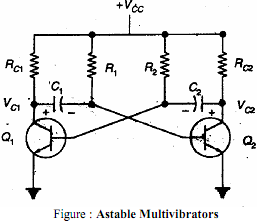
Once that happens, that transistor will turn on, thereby turning the other one off. If we pick a moment when Q1 has just turned off and Q2 is on, then the left end of C2 is at -5 volts. This negative voltage decreases as C2 charges through R2 towards +5 volts. However, the moment C2 charges enough to provide forward bias to the base of Q1, Q1 turns on and the 5 volt drop in Q1's collector voltage is coupled through C1 to the base of Q2. This turns Q2 off at once. As we saw in the previous experiment, the time that Q1 remains on and Q2 remains off is 0.693RC, which for the component values shown here is about 1 second.
Now Q2 is held off while C1 charges through R1, until Q2's base becomes forward biased. At that point the transistors switch states again and the whole thing starts over. There is no stable state where the circuit can come to rest, so this circuit is known as an astable multivibrator.
The time Q2 remains off is set by R1 and C1, just as the time Q1 remains off is set by R2 and C2. For our circuit, the components are of the same values on each side, so the timing will be the same on each half of the cycle. This is not required; the two halves of the circuit can have totally different time intervals. They actually operate independently of each other, even though they work together.
Since this particular circuit will spend about 1 second on each half cycle, the total cycle time, or period, is about 2 seconds. The operating frequency of the circuit is the reciprocal of the period, or 0.5 Hz.