The Water Cycle:
The importance of water is obvious to everyone. Water is synonynlou. with life. The most comnlon substance in the body of iinv organism is water. It is also the most abundant substance .in our environment. An estimatcd amount of'1500 million cubic kilometers of water, in one form or the other, is present in the biosphere. Ocean is the major reservoir of water which covers about seventy per cent of earth's surface. Ocean water is salty. Fresh water is mostly found in rivers and in between rocks below the surface of the earth. The water cycle is driven by the sun's heat energy, which causes water to evaporate, while gravity draws the water back to earth after water vapour condenses. Here, we would like to point out a difference between the water cycle, and the two previous cycles. Unlike in nitrogen and carbon cycles, most of the forces that cause water to be cycled do not involve organisms, but are the normal physical processes, like evaporation, condensation etc. In this unit, water cycle is divided into 4 basic steps. Before we proceed further, you may go through Fig. 14.8 carefully, and then read the corresponding description as you did for the study of nitrogen and carbon cycle.
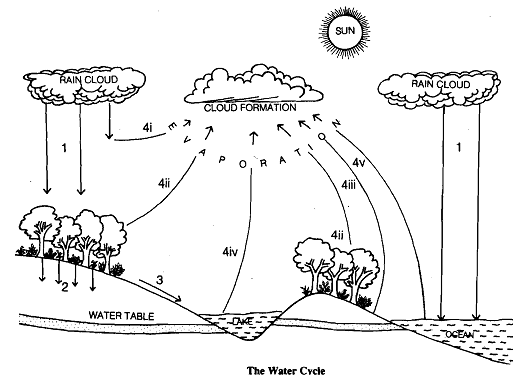
1) All water, which is used by mankind for personal and industrial purposes, is plain or fresh water, which is derived largely from the ocean water through evaporation and precipitation.
2) As the precipitation reaches the earth, some of the water falls directly on the ground, some falls on vcgctation, on buildings and on strccts. A part of the watcr that falls on Lhc ground, seeps through the soil, to an impervious layer of cla.1 or rock and collects as groundwater. The rate of downward movement of water in soil is dependent on the type of soil, its slope, type of vegetation and the amount of rainfall. The underground water is utilised by human beings for domestic, agricultural or industrial purposes.
3) Some of the water falling on the ground runs down the gutters and drains to be carried off to rivers. Some surface runoff may also collect in small ditches, lakes etc.
4) So far we have been discussing the various ways in which water, in different forms, reaches the earth. Now let us understand as to how water reaches back to the atmosphere.
i) Some amount of rain water never reaches the ground as it evaporates back into the atmosphere.
ii) Plants also give out large amounts of water back to the atmosphere through their leaves.
iii-v) The water remaining on the surface of the ground and on vegetation as well as the water in the surface layers of streams, lakes mad oceans evaporates and goes back to the atmosphere. As the water vapours in the atmosphere form clouds and drift with wind,'they eventually meet cold air and condense in the same way as moisture from the air in the room condenses outside a glass of iced water.