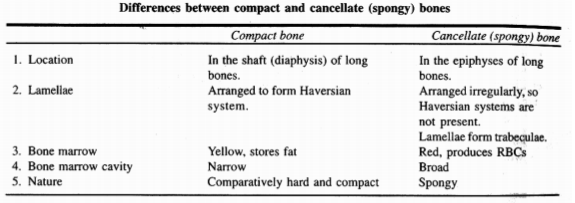
TYPES OF BONE -
On the basis of its texture, a bone is of two types -
- Spongy or cancellous or tubercular bone and
- Compact or periosteal or dense bone.

Ossification (Bone formation)
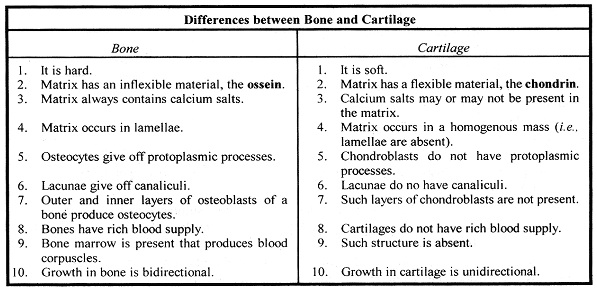
The skeleton is formed entirely of cartilage in an early embryo.
The process of bone formation is called ossification or osteogenesis.
Bones are of the following types according to their source of formation -
1. Cartilaginous or Replacing Bones -
- These bones develop from the pre-existing cartilage and practically replace the cartilage.
- They are also called endochondrial bones. Examples: humerus, femur.
2. Investing or Dermal or Membrane Bones -
- These bones develop in the dermis of the skin as thin plates and sink to get attached over the original cartilaginous endoskeleton.
- In fact these bones become invested upon original cartilages hence their name.
- Examples: frontal, nasals, vomers and parietals of the skull.
3. Sesamoid Bones -
- These bones are formed in the tendons at the joints. Example: patella (knee-cap).
4. Visceral Bones -
- These are formed in the soft organs (= viscera).
- Examples:
os cordis in the heart of some ruminants (e.g., deer),
os penis in the penis of most bats, insectivores, rodents (e.g., rats), carnivores (e.g., dog,walrus), whales, some primates (not man),
os clitoris in the clitoris of many carnivores, and
os palpebrae in the eyelids of crocodiles.
- A small bone also develops in the crest of a bird and snout of a hog.
OSTEOCLASTS -
- These cells are derived from osteoblasts and osteocytes, rich in acid phosphatase and contain slightly basophilic cytoplasm and are lysosome-rich, multinucleate cells which destroy bone matrix.
- They are also called bone destroying cells.
OSTEOMYELITIS -
- Inflammation of the bone marrow and adjacent bone and epiphysial cartilage.
PAGET'S DISEASE-
- Irregular thickening and softening of bones. A bone kept in KOH remains unaffected
OSTEOMYELODYSPLASIA
- Enlargement of the bone marrow cavities, thinning of the osseous tissue, thinning of osseous tissue, large thin- walled vascular spaces, leukopenia (fall in WBC count) and irregular fever.
- When required, calcium and phosphate are released from the bone into the blood under the influence of the hormones, parathormone from the parathyroid glands and calcitonin from the thyroid gland.