The Mean Value Theorem
Assume f(x) is a function that satisfies both of the subsequent.
1. f(x) is continuous on the closed interval [a,b].
2. f(x) is differentiable on the open interval (a,b).
So there is a number c such that a < c < b and
f'(c) = (f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)
Or f(b) - f(a) = f'(c) (b - a)
Proof
For illustration reasons let's assume that the graph of f(x) is,
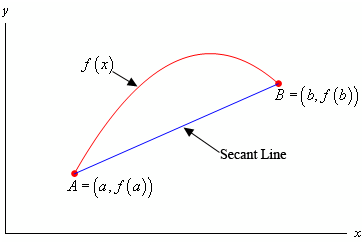
Note certainly that this may not seem as this, but we just require a fast sketch to make this easier to notice what we're talking about now.
The first thing is which we require is the equation of the secant line that goes through the two points A and B as demonstrated above. It is,
y = f(a) + ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)) (x -a)
Let's here define a new function, g(x), as to be the difference among f(x) and the equation of the secant line or,
g(x) = f(x) - (f(a) + ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)) (x -a))
= f(x) - f(a) - (f(b) - f(a))/(b -a) (x -a))
Next, let's see that g(x) is the total of f(x) that is assumed to be continuous on [a,b], and a linear polynomial, that we know to be continuous all over, we know that g(x) should also be continuous on [a,b].
Also, we can notice that g(x) should be differentiable on (a,b) since this is the total of f(x), that is assumed to be differentiable on (a,b), and a linear polynomial, that we know to be differentiable.
We could also have only calculated the derivative as follows,
g'(x) = f(x) - (f(a) + ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a))
At that point we can notice that this exists on (a,b) as we assumed that f′(x) exists on (a,b)and the last term is only a constant.
At last, we have,
g(a) = f(a) - (f(a) + ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)) (a -a))
= f(a) - f(a) = 0
g(b) = f(b) - (f(a) + ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)) (b -a))
= f(b) - f(a) -(f(b) - f(a))= 0
Conversely, g(x) satisfies the three conditions of Rolle's Theorem and therefore we know that there should be a number c as a < c < b and that,
0 = g'(c) = f'(c) - ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a)) => f'(c) = ((f(b) - f(a))/(b -a))