STRUCTURE
- Each chromosome composed of two interwoven (coiled) threads called Chromonema (Chromonemata) embeded in a matrix of semisolid protein.
- Surface of matrix is in form of a membrane called Pellicle.
- Chromonema name proposed by Vejdowsky.
- Each Chromonema is composed of a single DNA molecule.
- Coiling of chromonema is of two types -
- Plectonemic coiling is characteristic of Mitotic Chromosomes (Prophase) while meiotic Chromosomes in prophase stage have paranemic coiling.
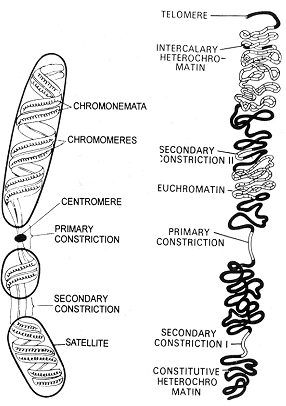
- Chromomeres - Dark granules on Chromonema.
- Chromomeres form due to extensive folding of DNA molecule.
- Two types of constrictions occur on Chromosome -
(1) Primary constriction or Centromere :- This is specialized and essential constriction on chromosome.
(i) Centromere remains unstained (Achromatic).
(ii) Pellicle is absent on centromere.
(iii) Each chromonema is associated with a disc shaped protein called Kinetochore. Centromere is essential for division of Chromosome and its movement towards poles during anaphase. Kinetochores provide attachment site to spindle fibers. Chromosome without centromere (Acentric) may last during cell division.
(2) Secondary constriction - It is ordinary constriction and it is nonessential part of Chromosome. In chromatin, sec. constriction occurs as heterochromatin.
- Part of Chromosome after sec. constriction is called Satellite body or Trabant.
- Nucleolar organiser is a type of satellite body.
- Chromosomes having satellite body are Called SAT chromosome (SAT = "Sine acid thymonucleinico" which refers to low DNA percentage)
- Satellite body of Chromosome have repetitive genes. Le. same type of genes are present many times.
- Nucleolar organiser is termed as sec. constriction-I and others as sec. constriction-II
- On the basis of position of Centromere, Chromosomes are of following types -
(i) Chromosomes which do not have centromere is called "Acentric."
(ii) On the basis of number of centromere chromosomes termed as Monocentric, diacentric and polycentric.
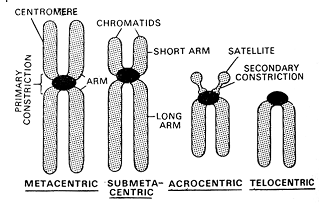
Based on the position of centromere chromosomes are of four types -
1. Telocentric - Centromere terminal
2. Acrocentric - Centromere inner to telomere
3. Submetacentric - Centromere submedian
4. Metacentric - Centromere median
ROBERT SOVIAN CHANGE
- If centromere of a metacentric chromosome is splitted then two telocentric chromosomes are formed such change is called Robert sovian change. It is a type of mutation.
- If arm of a telocentric chromosome is splitted upto centromere then a metacentric chromosome with two identical arms is formed. Such Chromosome is called Isochromosome.