Solid-State Control of Synchronous Motors
The speed of a synchronous motor can be controlled by changing its supply frequency. With variable-frequency control, two modes of operation are possible: true synchronous mode, employed with voltage source inverters, in which the supply frequency is controlled from an independent oscillator; and self-controlled mode, in which the armature supply frequency is changed proportionally so that the armature field always rotates at the same speed as the rotor. The true synchronous mode is used only in multiple synchronous-reluctance and permanent-magnet motor drives, in applications such as paper mills, textile mills, and fiber-spinning mills, because of the problems associated with hunting and stability. Variable-speed synchronous-motor drives, commonly operated in the self-controlled mode, are superior to or competitive with induction motor or dc-motor variable-speed drives.
Drives fed from a load-commutated current-source inverter or a cycloconverter find applications in high-speed high-power drives such as compressors, conveyors, traction, steel mills, and ship propulsion. The drives fed from a line-commutated cycloconverter are used in low-speed gearless drives for mine hoists and ball mills in cement production. Self-controlled permanent- magnet synchronous-motor drives are replacing the dc-motor drives in servo applications.
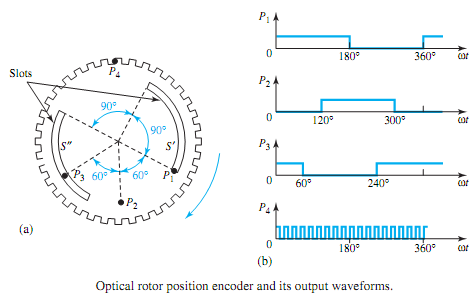
Self-control can be applied to all variable-frequency converters, whether they are voltage- source inverters, current-source inverters, current-controlled PWMinverters, or cycloconverters. Rotor position sensors, i.e., rotor position encoders with optical or magnetic sensors, or armature terminal voltage sensors, are used for speed tracking. In the optical rotor position encoder shown in Figure for a four-pole synchronous machine, the semiconductor switches are fired at a frequency proportional to the motor speed. A circular disk, with two slots S� and S�� on an inner radius and a large number of slots on the outer periphery, is mounted on the rotor shaft. Four stationary optical sensors P1 to P4 with the corresponding light-emitting diodes and photo transistors are placed as shown in Figure. Whenever the sensor faces a slot, an output results.Waveforms caused by the sensors are also shown in Figure. A detailed discussion of this kind of microprocessor control of current-fed synchronous-motor drives is outside the scope of this text.