Q. Show Power and Power Factor in ac Circuits?
Power is the rate of change of energy with respect to time. The unit of power is a watt (W), which is a joule per second (J/s). The use of rms or effective values of voltage and current allows the average power to be found from phasor quantities. Let us consider a circuit consisting of an impedance Z φ = R + jX excited by an applied voltage of v(t) = √2 Vrmscos (ωt + φ), producing a current of i(t) =√2 Irmscosωt . The corresponding voltage and current phasors are then given by V φ and I0°, which satisfy the Ohm's-law relation ¯ V/ ¯ I = V φ/I 0° = Z φ.
The instantaneous power p(t) supplied to the network by the source is

which can be rearranged as follows by using trigonometric relations:
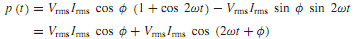
Atypical plot of p(t) is shown in Figure, revealing that it is the sumof an average component, VrmsIrms cos φ, which is a constant that is time independent, and a sinusoidal component, VrmsIrms cos(2ωt +φ), which oscillates at a frequency double that of the original source frequency and has zero average value. The average component represents the electric power delivered to the circuit, whereas the sinusoidal component reveals that the energy is stored over one part of the period and released over another, thereby denoting no net delivery of electric energy. It can be seen that the power p(t) is pulsating in time and its time-average value P is given by Pav = Vrms Irms cos φ since the time-average values of the terms cos 2ωt and sin 2ωt are zero. Note that φ is the angle associated with the impedance, and is also the phase angle between the voltage and the current.
The term cos φ is called the power factor. An inductive circuit, in which the current lags the voltage, is said to have a lagging power factor, whereas a capacitive circuit, in which the current leads the voltage, is said to have a leading power factor. Notice that the power factor associated with a purely resistive load is unity, whereas that of a purely inductive load is zero (lagging) and that of a purely capacitive load is zero (leading).