Ratio Test
In this part we are going to take a look at a test that we can make use to see if a series is absolutely convergent or not. Remind that if a series is absolutely convergent after that we will also know that it's convergent and thus we will frequently use it to simply find out the convergence of a series.
Previous to proceeding with the test let's do a quick reminder of factorials. This test will be specifically useful for series that consist of factorials (and we will see some in the applications) thus let's make sure we can deal along with them before we run into them in an instance.
If n is an integer like n ≥ 0 then n factorial is illustrated as,
n! = n(n-1) (n-2) ... (3) (2)(1) if n > 1 by definition
0! = 1
Let's calculate a couple real quick.
1! =1
2! = 2(1) = 2
3! = 3 (2)(1) = 6
4! = 4 (3) (2) (1) = 24
5! = 5 (4) (3) (2) (1) = 120
In the final computation above, note that we could rewrite the factorial in a couple of different ways. For example,
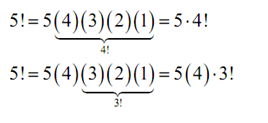
Generally we can always "strip out" terms from a factorial like this.
n! = n (n-1) (n-2) ... (n-k) (n- (k+1)).... (3) (2) (1)
= n (n-1) (n-2) ... (n-k). (n- (k+1))!
= n (n-1) (n-2) ... (n-k). (n- k-1)!
We will require to do this on occasion so don't forget about it.
As well, when dealing with factorials we need to be very cautious with parenthesis. Example for this, (2n)! ≠ 2 n! as we can see if we write each of the subsequent factorials out.
(2n)! = (2n) (2n-1) (2n-2) ... (3) (2) (1)
2 n! = 2 [(n) (n-1) (n-2).... (3) (2) (1)]