Question: Product differentiation and entry/exit
Two differentiated goods, apples and oranges, are located at the two extremes of a linear product space (a segment of length 1) (i.e., apples at 0 and oranges at 1). The price of apples is p1, the price of oranges is p2. The utility of a consumer located at t that consumes one apple is
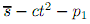
The utility of a consumer located at t that consumes one orange is
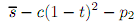
The utility of a consumer located at t that consumes nothing or both apples and oranges is zero. Consumers are located uniformly along the segment. (This is exactly like the transportation model, where spatial preferences are reinterpreted as tastes and 'transportation costs' are quadratic.). The unit cost of transportation is c. The marginal cost of each good is μ. Assume that Firm 1 is an apple monopoly, ?rm 2 is an orange monopoly.
(a) Calculate the demand functions for apples and oranges. For what ranges of prices the demands are well de?ned?
(b) Consider the demand functions for apples and oranges that you have calculated in the previous part. Assume that ?rms set prices simultaneously. Write the maximization problem of ?rm 1 and ?rm 2.
Solve for the Bertrand equilibrium. Compute prices, equilibrium quantity demanded and the pro?ts.
Suppose now that ?rm 1 is an apple monopoly, but that both ?rms produce oranges.
(c) Compute the equilibrium. Show that the pro?tof ?rm1issmaller(by a factor of4)than in part
(b). Explain step by step.
(d) Suppose that there are no exit costs, that entry costs are sunk, that ?rm1 is in bothmarkets,and that ?rm 2 is in the orange market (as in part (c)). Which ?rm has an incentive to exit the orange market? What do you conclude about the role of sunk costs or exit costs with regard to the possibility of entry deterrence through product differentiation (e.g., ?rm 1 entering ?rst in orange markets).