Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?
Accounting Cost versus Economic Cost
- Accounting Cost
- Actual expenses and adding the depreciation charges for the capital equipment
- Economic Cost
- Cost to a firm of employing economic resources in production, involving the opportunity cost
Opportunity cost.
- Cost associated with opportunities that are foregone when a firm's resources are not put to their highest-value use.
An Example
- A firm has its own building and pays no rent for the space of office
- Does this mean cost of office space is zero?
Sunk Cost
- Expenditure which are made already and cannot be recovered back
- Should not influence firm's decisions.
An Example
- A firm pays $500,000 for option to buy building.
- The cost of building is $5 million or total of $5.5 million.
- The firm finds the other building for $5.25 million.
- Which building should the firm buy?
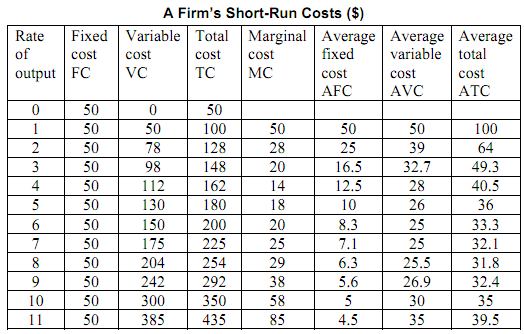
Fixed and Variable Costs
- Total output is the function of variable inputs and fixed inputs.
- Thus, the total cost of production equals fixed cost (cost of the fixed inputs) plus variable cost (the cost of the variable inputs)
- Fixed Cost
- Does not vary with level of output
- Variable Cost
- Cost which varies as the output varies
Fixed Cost
- Cost paid by firm which is in business regardless of level of output
Sunk Cost
- Cost that have been incurred and recovering of it can't be done
?Personal Computers: most costs are variable
- Components, labor
Software: most costs are sunk
- Cost of developing the software
Pizza
- Largest cost component is fixed