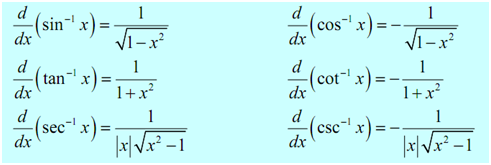Inverse Tangent : Following is the definition of the inverse tangent.
y = tan -1 x ⇔ tan y = x for -∏/2 ≤ y ≤ ?/2
Again, we have a limitation on y, however notice that we can't allow y be either of the two endpoints in the limitation above since tangent isn't even described at those two points. In order to convince yourself that this range will cover all possible values of tangent do a quick sketch of the tangent function and we can see that in this range we do indeed cover all possible values of tangent. Also, in this case there is no limitation on x since tangent can take on all possible values.
Example Evaluate tan -1 1
Solution : Following we are asking,
tan y =1
where y satisfies the limitation given above. From a unit circle we can illustrated that
y = ∏ /4.
Since there is no limitation on x we can ask for the limits of the inverse tangent function as x goes to plus or minus infinity. In order to do this we'll require the graph of the inverse tangent function. This is illustrated below.
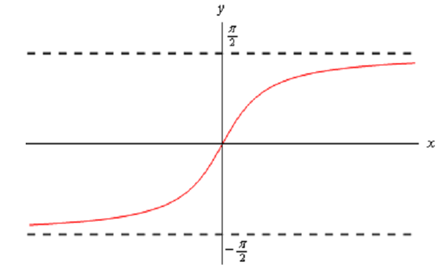
From this graph we can illustrates that

The tangent & inverse tangent functions are inverse functions hence,
tan ( tan -1 x )= x tan -1 ( tan x ) =x
Thus to determine the derivative of the inverse tangent function we can begin with
f ( x ) = tan x g ( x ) = tan -1 x
Then we have,
g′ ( x ) = 1 /f ′ ( g ( x )) = sec2 (tan -1 x )
Simplifying the denominator is alike to the inverse sine, however different sufficient to warrant illustrating the details. We'll begin with the definition of the inverse tangent.
y = tan -1 x ⇒ tan y = x
Then the denominator is,
sec2 (tan -1 x ) = sec2 y
Now, if we begin with the fact that
cos2 y + sin 2 y = 1
and divide every term by cos2 y we will get,
1 + tan 2 y = sec2 y
Then the denominator is,
sec2 (tan -1 x ) = sec2 y = 1 + tan 2 y
At last by using the second portion of the definition of the inverse tangent function specified us,
sec2 ( tan -1 x ) = 1 + tan 2 y = 1 + x2
Then the derivative of the inverse tangent is,
d (tan -1 x ) / dx =1 /1 + x2
There are three more inverse trig functions however the three illustrated here the most common ones. Formulas for remaining three could be derived through a similar procedure as we did those above.
Following are the derivatives of all six inverse trig functions.