HYSTERESIS LOOP:
A ferromagnetic material retains some magnetism after the magnetising force is removed. The BH curve (O to Q) will therefore only be followed once, on initial magnetisation.
When a material is subjected to a changing magnetising force, the flux density is affected by its previous magnetic history. There is tendency for the magnetic conditions to lag behind the magnetising force that is producing them. This is known as 'hysteresis' and comes from the Greek meaning late or lagging.
If a piece of material is taken through a complete cycle of magnetising and demagnetising the graph of B against H is as shown, this diagram is called a hysteresis loop.
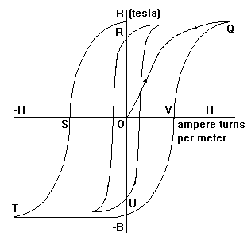
O to Q - Initial magnetisation to saturation at point A
Q to R - Magnetising force is reduced to zero.
O to R - Represents remanence. Remanence is the flux density remaining in
or the material after the magnetising force is removed. It is sometimes
0 to U called 'retentivity'. If the material had not been taken to saturation then OR or OU would represent the remanent flux density.
R to S - The magnetising force is reversed.
O to S - Represents the magnetising force required to reduce the flux density
or to zero. This is called the coercivity of the material. If the material
O to V had not reached saturation it is termed the 'coercive force'.
S to T - Further increase in the reverse magnetising force. This causes the material to reach saturation in the opposite direction.
T to Q - Reversal of magnetising force again eventually makes the material saturate in original direction.
The term residual magnetism is used to describe the useful flux remaining after the magnetising force has been removed for a considerable time. It is proportional to the coercivity of the material and is also called coercivity. This term should not be confused with remanence or remanent flux density.
The area of the loop represents the energy loss during each magnetic cycle, or the power dissipated. It's size is dependent upon the type of material and frequency at which the magnetising force is switched.
The following should be noted:
- Soft iron saturates with much less magnetising force than steel.
- The remanence of soft iron is greater than that of steel.
- The area of the loop and coercivity for steel is much greater than for soft iron. This indicates greater hysteresis loss and residual magnetism.
- Materials with large loops are used for permanent magnets - ticonal.
- Materials with small loops are used for temporary magnets - stalloy, Mumetal.