How call processing takes place?
Fundamental Call Procedure: Fig. demonstrates a simplification diagram exemplifying how two telephone sets (as subscribers) are interconnected by a central office dial switch. All subscribers are connected to the switch by a local loop. The switch is most probable some sort of an electronic switching system (i.e. ESS machine). The local loop are terminated on the calling and called stations into telephone sets and on the central office ends to switching machines.
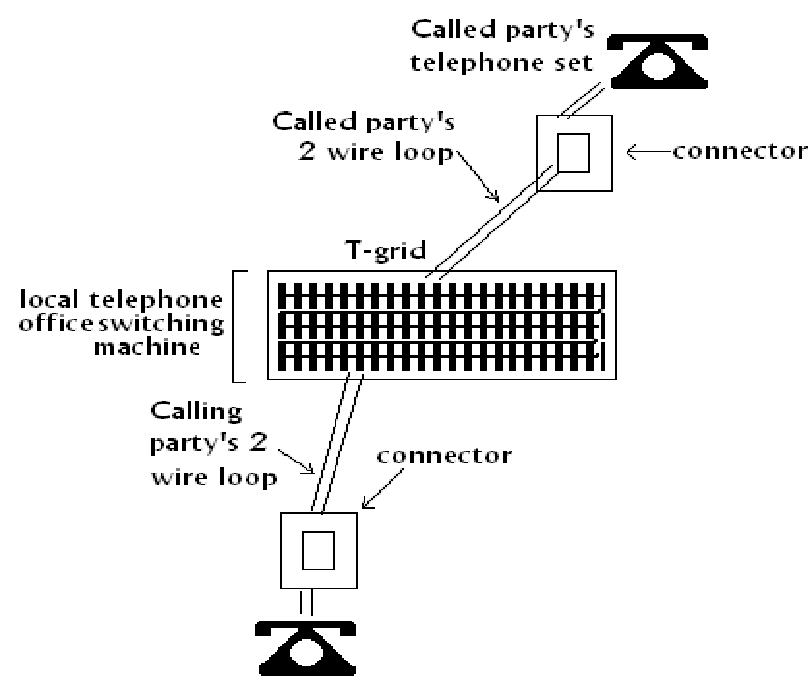
FIG - Telephone Call Procedure
Whenever the calling party's telephone set goes off hook (that is, lifting the handset off the cradle), the switch hook into the telephone set is released, completing a dc path in between the ring and the tip of the loop trough the microphone. An electronic switching system machine senses a dc current in the loop and recognizes it as an off-hook condition. Completing a local telephone call among two subscribers connected to the similar telephone switch is accomplished by a standard set of procedure which includes the 10 steps listed next.
1. Calling station goes off hook.
2. After detecting a dc current flow at the loop, the switching machine returns an audible dial tone to the calling station, acknowledging as the caller has access to the switching machine.
3. The caller dials the destination telephone number by using one of the two ways: Mechanical dial pulsing or, more probably, electronic double-tone multi frequency (Touch-Tone) signals.
4. Whenever the switching machine senses the first dialled number, this removes the dial tone from the loop.
5. The switch interprets the telephone number and after that locates the loop for the destination telephone number.
6. Before ringing the destination telephone, the switching machine tests the destination loop for dc current to notice if this is idle (on hook) or in utilize (off hook). Simultaneously, the switching machine locates a signal path by the switch among the two local loops.
7. (a) When the destination telephone is off hook then the switching machine sends a station busy signal back to the calling station.
(b) When the destination telephone is on hook so the switching machine sends a ringing signal to the destination telephone on the local loop and similar time sends a ring back signal to the calling station to provide the caller any assurance that something is occurrence.
8. If the destination answers the telephone, this completes the loop, causing dc current to flow.
9. The switch knows the dc current as the station answering the telephone. Now, the switch removes the ringing and ring-back signals and finishes the path by the switch, permitting the calling and called parties to start conversation.
10. If either end goes on hook, the switching machine senses an open circuit on which loop and after that drops the connections by the switch.