Q. Forces and torques in magnetic-field systems?
We mentioned earlier that the greater ease of storing energy in magnetic fields largely accounts for the common use of electromagnetic devices for electromechanical energy conversion. In a magnetic circuit containing an air-gap region, the energy stored in the air-gap space is several times greater than that stored in the iron portion, even though the volume of the air gap is only a small fraction of that of the iron.
The energy-conversion process involves an interchange between electric and mechanical energy via the stored energy in the magnetic field. This stored energy, which can be determined for any configuration of the system, is a state function defined solely by functional relationships between variables and the final values of these variables. Thus, the energy method is a powerful tool for determining the coupling forces of electromechanics.
In a singly excited system, a change in flux density from a value of zero initial flux density to B requires an energy input to the field occupying a given volume,
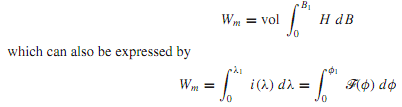
Note that the current i is a function of the flux linkages λ and that the mmf F is a function of the flux φ; their relations depend on the geometry of the coil, the magnetic circuit, and the magnetic
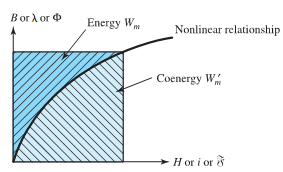
properties of the core material. Equations may be interpreted graphically as the area labeled energy in Figure. The other area, labeled coenergy in the figure, can be expressed as
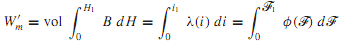
For a linear system in which B and H, λ and i,or φ and F are proportional, it is easy to see that the energy and the coenergy are numerically equal. For a nonlinear system, on the other hand, the energy and the coenergy differ, as shown in Figure, but the sum of the energy and the coenergy for a singly excited system is given by
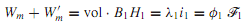
The energy stored in a singly excited system can be expressed in terms of self-inductance, and that stored in a doubly excited system in terms of self and mutual inductances, for the circuit- analysis approach, as we pointed out earlier.