In Bontemps, Louisiana there are only two places to spend time: Merlotte's bar and Fangtasia. Sookie and Eric have made plans to spend Friday night together, but they never decided where they would go. Both Sookie and Eric like each other and will not enjoy their evening if it is spent alone. However, given that they spend the evening together, Eric prefers to go to Fangtasia, and Sookie prefers to go to Merlotte's. If both Eric and Sookie go to Fangtasia, Eric gets payoff 2; if Both Eric and Sookie go to Merlotte's, Sookie gets payoff 2. Eric's payoff if both he and Sookie meet at Merlotte's (his less preferred activity) depends on how much Eric likes Sookie, represented by Eric's type e, which is known only to Eric. Similarly, if Sookie and Eric meet at Fangtasia, Sookie's payoff depends on how much she likes Eric, represented by her type, s, which is known only to her. Both players believe that the other player's type is uniformly distributed between zero and one, Pr (s < x) = Pr (e < x) = x.
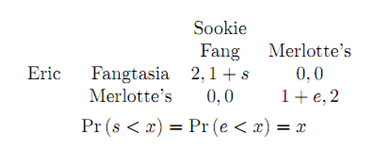
(a) Suppose that Eric believes that Sookie will go to Merlotte's if her type s is less than s and will go to Fangtasia if her type is bigger than s*.
What is the probability that Sookie will go to Merlotte's? What is the probability that she will go to Fangtasia?
(b) What is Eric's expected payoff if his type is e and he goes to Fangtasia? What is his expected payoff if he is type e and goes to Merlotte's?
(c) What is Eric's best response to Sookie's strategy? (For which values of e does he go to his preferred activity? For which values of e does he go to Sookie's preferred activity?) Explain.
(d) Find a Bayesian Nash equilibrium in which Eric goes to Fangtasia if his type e is less than e*; and Sookie goes to Merlotte's if her type s is less than s*: Assume that the equilibrium is symmetric e* = s*.
(e) For what combinations of types (s; e) do Eric and Sookie spend Friday night together? What is ironic or peculiar about your answer? (Hint: describe what would happen if Sookie and Eric both like each other a lot)