Explain the Population Growth?
A population can grow, it can remain stable, or it can decrease in size. Measuring the size of a population over time is used to help determine the factors at work and understanding the overall processes involved in populations. Thomas Malthus idea that plants and animals increase geometrically, yet do not cover the entire surface of the Earth because of natural limitations, told us that populations usually do not increase at a rate unchecked, but remain more or less stable over time. Population ecologists usually measure a populations intrinsic rate of natural increase under ideal conditions by applying the following mathematical formula:
Where N represents the total number of individuals in the population, dN/dt refers to the rate of change (in numbers of individuals) over time, and ri stands for the intrinsic rate of natural increase of the population. This relationship depicts the populations inherent potential for growth under ideal conditions. That is to say, if there were no restrictions to growth such as disease, predation, etc. This actually is a simple formula. You first determine the initial population size (in numbers of individuals) (= N1). Determine what the population would be due to unrestricted reproduction say after a one-year period (=N2). Determine the difference in size (N2 - N1 = dN). The period of time = dt. dN/dt gives you the rate of change over time.
Sometimes the intrinsic rate of natural increase is synonymous with biotic potential. Thus, the ideal birth rate minus the death rate indicates the maximum possible, or potential rate of increase for a population. Other factors such as movement of individuals into the population (referred to as migration), as well as movement of individuals out of the population (emigration) must also be taken into account when calculating rates of growth.
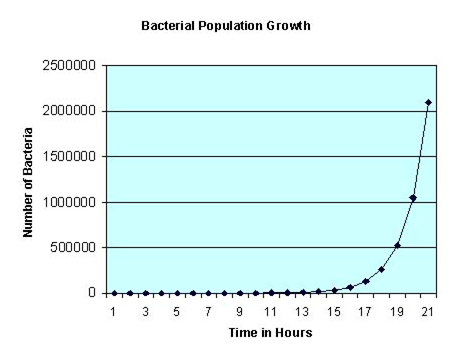
The intrinsic rate of natural increase is exponential for all populations. Remember, this growth rate does not allow for any negative factors that would decrease the population. For instance, if bacteria in a sterile nutrient broth divide every 30 minutes, the numbers of bacteria within the population would double every half hour starting with a single bacterium: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16,384, and so on. If you were to plot this growth curve, it would look like this:
Note that the shape of the growth curve forms a definite J shape. This shape typifies exponential growth, where it starts off very slowly with a gentle slope, and then doubles with each successive generation. This rapid growth rate does not last long under real conditions, as some critical factor ultimately becomes limiting. Malthus pointed out long ago that there are reasons why elephants do not cover every square inch of the Earth!
If a population of 1000 lemmings reproduced 244 young on average every year, and natural death claimed 200 lemmings on average every year, the difference between births and deaths would be + 44. Since the average birth rate is 244/1000, and the death rate is 200/1000, the difference yields the average growth rate per 1000 per year. If you simplify + 44/1000 per year, you would divide + 44 by 1000 to arrive at the average growth rate per individual per year, which works out to + 0.044. Thus, if you were studying a lemming population of 10,000, this populations intrinsic rate of growth would be + 440 individuals per year.