Explain the Kinetic Theory
Kinetic theory looks at how each of these steps adds more internal kinetic energy (jiggle energy) to the material. A solid is a framework of atoms and/or molecules that are fairly rigidly attached to one another. At first, as you add heat, the atoms and molecules jiggle more but stay in their place in the structure and the material on average takes up more and more room as the solid's temperature increases. (Compare this to a group of 25 three year olds who are seated in a circle but wiggling more and more without changing places.) When enough heat is added, the atoms and molecules break apart the attachments of this structure. These atoms and molecules can then move past each other and the solid changes into a liquid. (The three year olds are no longer in a group but moving in a line across the room, and some rearrangement happens in the line as it moves.) The liquid will take up more and more room as each atom or molecule jiggles faster and the temperature of the liquid increases. While the atoms and molecules are no longer closely related with one another, all bonds have been broken and the liquid has turns into a gas. (The three year olds are let outside for recess.) In a gaseous state, every atom or molecule is no longer surrounded by various neighbors, but infrequently bumps into another atom or molecule. Like the gas atoms or molecules move very fast and faster, the gas will take up more room.
( After the three year olds are let outside, children will start moving faster and faster and will fill up the playground.)
At every step when heat is being added, either the temperature of the material is rising or the material is changing phases with no any change in temperature. Equation (8.1) covers the temperature changes but we also need to be able to compute the heat needed to change phases. In melting, or going from solid to liquid, it takes an amount of heat
Qf = m Hf (8.2)
to change from a solid to a liquid. Qf is the amount of heat to melt the solid in kcal, m is the mass of the solid in kg, and Hf is the heat of fusion in kcal/kg. In evaporating, or changing from a liquid to a gas it takes an amount of heat
Qv = m Hv (8.3)
to change from a liquid to a gas. Qv is the amount of heat to evaporate the liquid in kcal, m is the mass of the liquid in kg, and Hv is the heat of vaporization in kcal/kg.
More rarely, the solid can change directly to a gas. This is called sublimation and is the reason that solid carbon dioxide, CO2, is used to keep ice cream frozen while it is being shipped. Dry ice, solid CO2, does not become a liquid but changes directly to gaseous CO2.
The amount of heat needed to turn a mass, m of ice at some initial temperature, Ti, into a gas at a final temperature, Tf, can be computed by
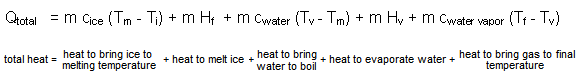
where Qtotal is the amount of heat to turn mass m (in kg) of ice at Ti (in Co) into gas at Tf (in Co), Tm is the melting temperature of ice, 0oC, cice, cwater, and cwater vapor are specific heats in kcal/kgCo, and Tv is the boiling temperature of water, 100oC. Temperatures could also be expressed in kelvins, since one kelvin is equal to one Co. Consequently, changes in temperature calculated in Co are equal to those calculated in kelvins. The same amount of heat, Qtotal, would be given up rather than absorbed if a mass, m, of water vapor at Tf is turned into ice at Ti .