Parallelism based on Grain size
Grain size: Grain size/ Granularity are a measure that defines how much computation is involved in a process. Grain size is concluded by counting number of instructions in a program segment. The subsequent types of grain sizes have been recognized (shown in Figure):
Figure: Types of Grain sizes
1) Fine Grain: This type includes nearly less than 20 instructions.
2) Medium Grain: This type includes nearly less than 500 instructions.
3) Coarse Grain: This type includes nearly greater than or equal to one thousand instructions.
Based on these grain sizes, parallelism may be classified at several stages in a program. These parallelism stages create a hierarchy according to which, lower the level the finer is granularity of process. The amount of parallelism reduces with raise in level. Each level according to a grain size requires scheduling overhead and communication. Following are parallelism levels (shown in Figure):
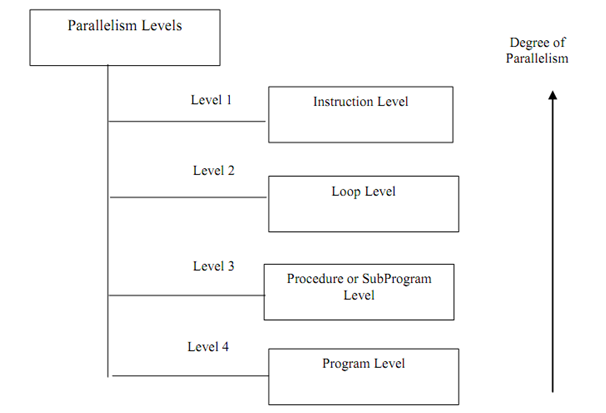
Figure: Parallelism Levels
1) Instruction level: It is the lowest level and degree of parallelism is highest at this level. Fine grain size is used at statement or instruction level as just few instructions make the grain size here. The fine grain size may perhaps vary according to type of the program. E.g. for scientific applications, Instruction level grain size may be higher. As the higher degree of parallelism is able to be achieved at this level, the overhead for a programmer would be more.
2) Loop Level: This is other stage of parallelism where iterative loop instructions able to be parallelized. Fine grain size is used at this stage too. Simple loops in program are simple to parallelize whereas the recursive loops are hard. This kind of parallelism can be achieved by the compilers.
3) Subprogram or Procedure Level: This level consists of subroutines, subprograms or procedures. Medium grain size is used at this level including several thousands of instructions in a process. Multiprogramming is applied at this stage. Parallelism at this level has been developed by programmers however not through compilers. Parallelism through compilers hasn't been attained at the medium and coarse grain size.
4) Program Level: It is the last level consisting of independent programs for parallelism. Coarse grain size is used at this stage including tens of thousands of instructions. Time sharing is attained at this level of parallelism. Parallelism at this stage has been exploited through the operating system.
The relation between parallelism levels and grain sizes has been shown in Table.

Table: Relation between grain sizes and parallelism
Coarse grain parallelism is conventionally applied in shared memory or tightly coupled multiprocessors such as the Cray Y-MP. Loosely coupled systems are used to perform medium grain program segments. Fine grain parallelism has been monitored in SIMD organization of computers.