Q. Explain Mirror - Lens Equation?
A central equation in optics relates the focal length, object distance and image distance for a thin lens or mirror. This equation is generally expressed as
1/f=1/p+1/q,
Where f is the focal length and p is the distance from the object to the lens and q is the distance from the lens to the image.
We are able to derive this equation from the following figure using simple geometry.
n the figure, the center of the lens is at 0. p is the distance from the lens to he object and q is the distance from the lens to the image. hi is the height of the image and ho is the height of the object and f is the distance from the lens to the focal point.
Using the similar triangles indicated by the alternate interior angles at 0, consisting of sides p and ho for the left and q and hi for the right, we find
Ho/hi=p/q.
Likewise, from the similar triangles indicated by the alternate interior angles at f , consisting of ho along the center line of the lens and f for the
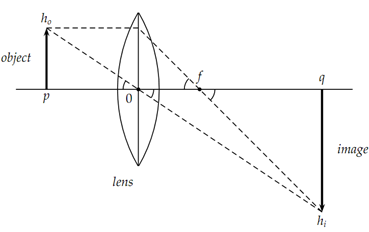
left and hi and q - f for the right, we find
ho/hi=f/(q - f)
Hence,
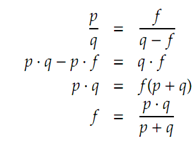
Finally,
1/f = (p + q) / (p* q) = 1/p + 1/q.
20.3 Lensmaker's Formula
Lenses with the same shape and index of refraction will have the same focal length. the lensmaker's formula relates the index of refraction, the radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens, and the focal length of the lens.
A number of idealizations, simplifications and approximations are used to complete the derivation, but the results are compact and sufficiently accurate for most purposes.
We begin by observing that a lens with convex surfaces behaves the same as two plano-convex lenses placed with the flat sides in contact. Fig. (20.3) shows the division of the lens into two pieces which we will analyze separately.
Recall that with thin lenses we are able to reverse the direction of the ray without affecting the incident and refracted angles. Represent one plano-convex lens may be regarded as the rightmost half of the original lens or the leftmost half reversed. The perpendicular ray enters the flat surface of the lens. It continues to the curved surface without initial refraction. When it appears from the curved surface it is refracted by an angle determined by Snell's law. The radius as of the centre of curvature extended through the exit point determines the surface normal. The angle in the media among the ray and the normal is θ1. The angle among the refracted ray and the normal is θ2.
If the index of refraction of the lens is n as well as we take the index of refraction of air as 1 Snell's law holds that
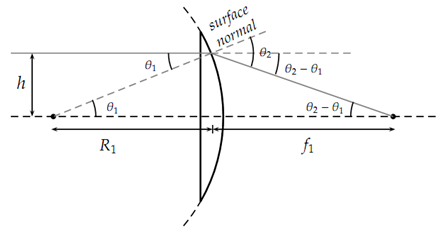
n sin θ1 = sin θ2.
Assuming small angles (paraxial rays), we now approximate the sines of the angles with the angles themselves so that
n θ1 ≈ θ2.
Substituting this in the angle among the refracted ray and the axis
θ2 - θ1 = n θ1 - θ1 = (n-1)θ1.
For these small angles the tangents are as well close to the angles themselves.
We can write
θ2 - θ1 ≈h/f1,
and
θ1 ≈h/R1.
1/f1 = (n-1)/R1.
Substituting from the lens equation which relates the object and image distances to the focal length
1/o1+1/i1=(n - 1)/R1.
The equivalent analysis of the other half of the lens gives
1/o2+1/i2=(n - 1)/R2.
We can now combine equations that noting that the image of the first lens is a virtual object for the second lens. Thus i1 = -o2 and, adding the two equations,
1/o1+1/i2= (n - 1) ((1/R1)+(1/R2)).
Writing the lens equation in terms of an object and the image distances
1/o+1/i=1/f.
However o1 and i2 are the object and image distances of the whole lens, so o1 = o and i2 = i. Thus,
1/f= (n - 1) ((1/R1)+(1/R2)).